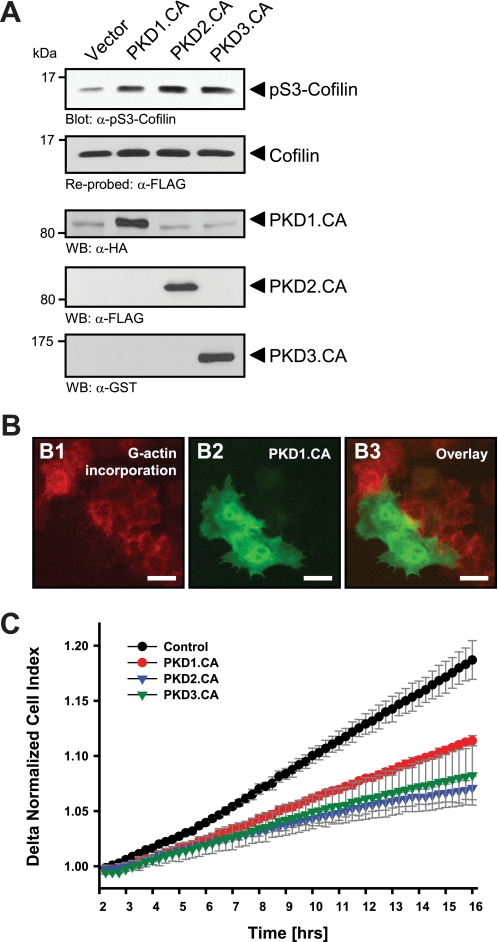
FIGURE 1.
Active PKD isoforms effectively inhibit cofilin activity and directed cell migration. A, HeLa cells (0.65 × 106 cells, 6-cm dish) were co-transfected with cofilin and control vector, constitutively active PKD1, PKD2, or PKD3 as indicated. Lysates were analyzed for cofilin phosphorylation at Ser-3 or total cofilin using α-pS3-coflin or α-FLAG antibodies, respectively. Expression of active PKD alleles was controlled using antibodies directed against their tags (α-HA for PKD1.CA, α-FLAG for PKD2.CA, and α-GST for PKD3.CA). B, free barbed end-induced actin incorporation at the leading edge is blocked by active PKD. HeLa cells (5 × 104 cells, 8-well ibiTreat μ-slide) were transfected with control vector or constitutively active GFP-tagged PKD1 (PKD1.CA). To analyze cofilin-mediated actin incorporation F-actin free barbed ends were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Scale bars are 20 μm. C, all active forms of PKD reduce directed cell migration. HeLa cells (5 × 105 cells, 6-cm dish) were transfected with control vector, constitutively active PKD1 (PKD1.CA), PKD2 (PKD2.CA), or PKD3 (PKD3.CA). After 2 h of attachment, cell migration toward NIH-3T3 conditioned medium over 14 h was monitored continuously in real-time using a Transwell CIM-plate 16 and the xCELLigence RTCA DP instrument. Error bars (gray) represent four experiments.