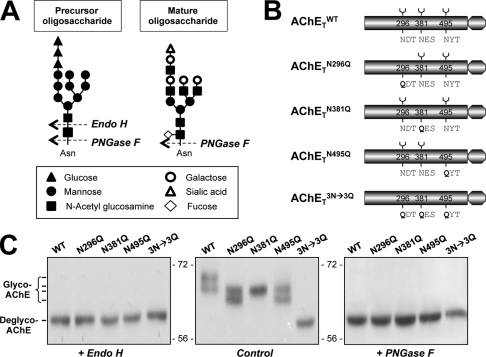
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of N-glycosylation of human AChET. A, representative cutting sites of Endo H and PNGase F are shown. N-Linked oligosaccharide chains share a chitobiose core (two N-acetyl glucosamine) linked to one side to an asparagine residue of a potential N-glycosylation site (Asn-X-Ser/Thr) and on the other side to a trimannosyl core (three mannose) that is linked to high mannose structure in precursor oligosaccharide or various complex sugar chains in mature oligosaccharide. Endo H specifically recognizes high mannose oligosaccharides, cleaving between the N-acetylglucosamine residues of the diacetylchitobiose core, whereas PNGase F cleaves all N-linked glycans attached to asparagine. A possible example is shown for illustration. B, shown are schematic representations of human AChET and its glycosylation site mutants. C, HEK293T cells were single-transfected with cDNAs encoding AChETWT, AChETN296Q, AChETN381Q, AChETN495Q, and AChETN296Q/N381Q/N495Q. The cell lysates were incubated with Endo H or PNGase F and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-AChE antibody. Representative gels from three independent experiments are shown (n = 3).