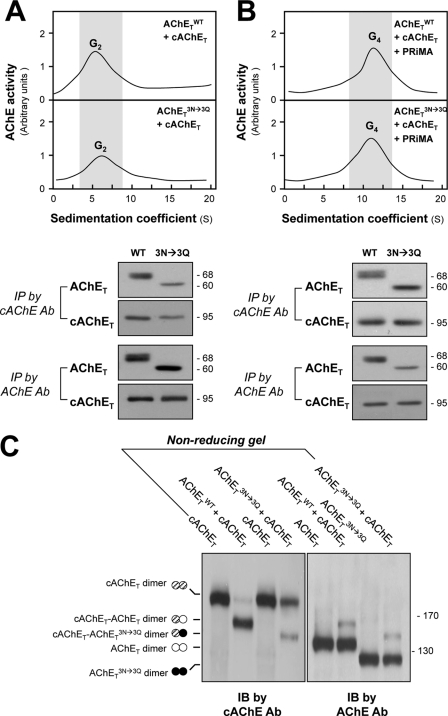
FIGURE 7.
N-Glycosylation is not required for the formation of human-chicken AChE dimers and tetramers. A, HEK293T cells were transfected with equal amounts of cDNAs encoding human AChET or AChETN296Q/N381Q/N495Q together with chicken AChET (cAChET). Equal amounts of protein from cell lysates were subjected to sucrose density gradient analysis. The enzymatic activities are plotted as a function of the S value, estimated from the position of sedimentation markers (upper panel). G2 fractions were collected for immunoprecipitation (IP) by either anti-human AChE antibody (Ab) or anti-cAChE antibody. The immunoprecipitated complexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-AChE and anti-cAChE antibodies, as indicated (lower panel). Both antibodies did not cross-react with other corresponding antigen. B, HEK293T cells were transfected with equal amount of cDNAs encoding AChET or AChETN296Q/N381Q/N495Q together with cAChET and PRiMA. Equal amounts of protein from cell lysates were subjected to sucrose density gradient analysis as in A. G4 fractions were collected for immunoprecipitation as in A. C, extracts from cells expressing AChETWT and cAChET separately or together were analyzed by non-reducing SDS-PAGE and labeled with anti-cAChE and anti-AChE antibodies. The presence of an intermediate band between cAChE and AChETN296Q/N381Q/N495Q dimers, recognized by both antibodies, demonstrates the formation of mixed cAChET-AChETN296Q/N381Q/N495Q dimers. IB, immunoblot.