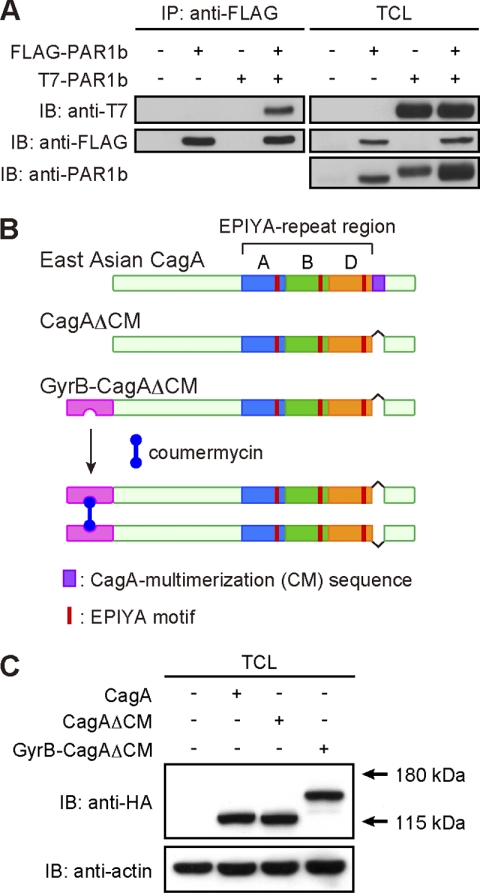
FIGURE 1.
Generation of conditionally dimerizable CagA. A, homodimerization of PAR1b in cells. Total cell lysates (TCLs) prepared from AGS cells transiently transfected with a FLAG-tagged PAR1b vector and/or a T7-tagged PAR1b vector were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody, and the anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates (IP) were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. B, strategy for chemical dimerization of CagA using the coumermycin-GyrB system. The 1–219-amino acid stretch of GyrB was fused to the N terminus of CagAΔCM, which lacks the CM sequence and thereby cannot bind to PAR1. Because coumermycin bivalently binds with GyrB, two GyrB-CagAΔCM mutants can be artificially dimerized in the presence of coumermycin. C, AGS cells were transiently transfected with an HA-tagged CagA, CagAΔCM, or GyrB-CagAΔCM expression vector. At 17 h after transfection, cells were harvested and lysed. TCLs were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.