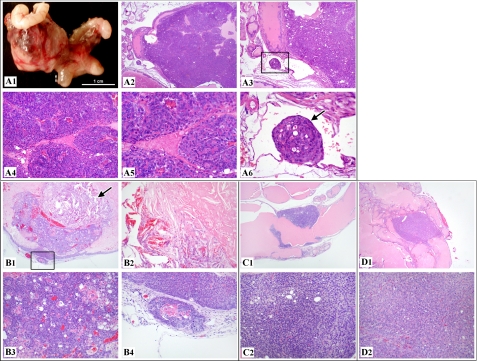
FIGURE 5.
Development of prostatic adenocarcinoma was observed in R26hARloxP/wt:Osr1-Cre+ and R26hARloxP/loxP:Osr1-Cre+. A, a 20-month-old R26hARloxP/wt:Osr1-Cre+ male mouse was grossly examined, which revealed a 1.8 × 1.3 × 1.3-cm mass at the base of the right seminal vesicle, replacing normal tissues of the right coagulating gland or anterior prostate area (A1). Histologically, the mass was an extensive, expansile, demarcated, unencapsulated neoplasm that intraluminally expanded a gland of the anterior prostate lobe (A2). The neoplasm consisted of haphazard solid lobules of cells with rare acinar formation (A4 and A5) with small amounts of fibrovascular stroma. The cells were pleomorphic with a large degree of anisocytosis and anisokaryosis, and occasional mitoses were noted. A tumor embolus was noted within an adjacent thin-walled vessel (A3 and A6). B, histologic analysis of a 19-month-old R26hARloxP/wt:Osr1-Cre+ male mouse revealed a focal, expansile, demarcated neoplasm filling the lumen of a gland of the anterior prostate (B1), with the remaining glandular mucosa demonstrating epithelial stratification consistent with high grade mPIN. The neoplasm consisted of haphazard acini of cells (B3) with small amounts of fibrovascular stroma. A sole, discrete invasive focus of the tumor is noted within the stroma next to the mass (B4), with the stroma presenting with an early desmoplastic response. A focal area of necrosis with abundant acicular (cholesterol) cleft formation is present within the main tumor mass itself (B2). C, histologic examination of a 34-week-old R26hARloxP/wt:Osr1-Cre+ male mouse revealed a likely circumferential, expansile, demarcated neoplasm focally expanding the mucosa of the anterior prostate gland (C1), with multifocal areas of the remaining glandular mucosa demonstrating epithelial cribriform changes consistent with high grade mPIN. The neoplasm consisted of haphazard solid sheet of cells with rare acinar formation (C2) with scant fibrovascular stroma. The cells were pleomorphic with a large degree of anisocytosis and anisokaryosis, and rare mitoses were noted. D, histologic assessment of a 80-week-old R26hARloxP/loxP:Osr1-Cre+ male mouse revealed a focal, expansile, demarcated neoplasm expanding the mucosa of the anterior prostate gland (D1), with multifocal areas of the remaining glandular mucosa demonstrating epithelial cribriform changes consistent with high grade mPIN. The neoplasm consisted of haphazard solid sheet of cells with rare acinar formation (D2) with scant fibrovascular stroma. The cells were pleomorphic, with a large degree of anisocytosis and anisokaryosis, and regular mitoses were noted.