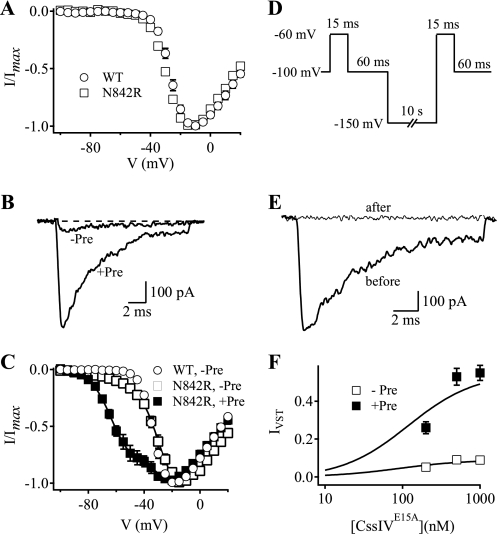
FIGURE 3.
Voltage sensor-trapping activity of CssIVE15A in N842R mutant channels. A, I-V plots obtained in the absence of toxin for WT rNav1.2a channels (circles) and N842R mutant channels (squares). B, IVST traces recorded during a 15-ms test pulse to −60 mV in the absence or presence of a 1-ms prepulse to +50-mV applied 60 ms earlier. C, I-V plots for N842R mutant channels in the presence of CssIVE15A with (filled squares) or without (open squares) the prepulse. The plot for WT channels without prepulse in the presence of toxin is shown for comparison (open circles). The solid lines are global fits to the I-V curves with Va1 = −27.6 mV, k1 = −7.0, Va2 = −61.4 mV, k2 = −7.9 mV. Without the prepulse, 7.5% of the current activated with the negative voltage dependence (Va2). With the prepulse, 55% of the current activated with the negative voltage dependence, Va2. D, voltage protocol used to observe the effects of hyperpolarization upon voltage sensor-trapping activity by CssIVE15A on N842R channels at resting membrane potential. E, IVST traces recorded at −60 mV before or after the hyperpolarization pulse to −150 mV for 10 s. F, concentration-response curves for IVST on N842R mutant channels by CssIVE15A with (filled squares, +Pre) or without (open squares, -Pre) the prepulse. IVST was normalized to the peak of the I-V in the absence of toxin. Concentration-response data were fit with first-order Hill equations (n > = 4).