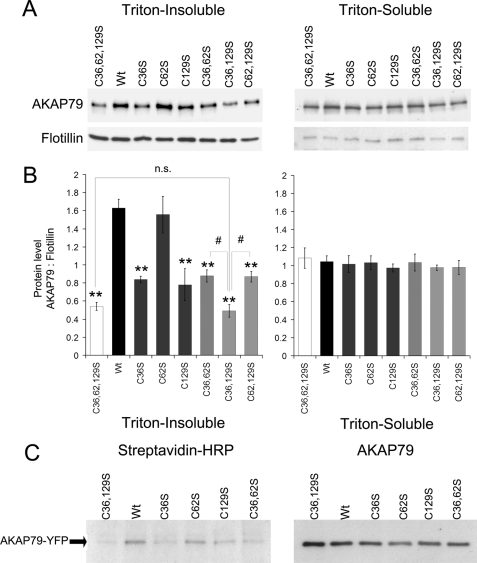
FIGURE 2.
Palmitoylation on cysteine 36 and 129 of AKAP79 promotes association with Triton-insoluble membranes. A, HEK-293 cells transiently expressing AKAP79-YFP wild type (Wt), single (C36S, C62S, and C129S), double (C36S,C62S (C36,62S), C36S,C129S (C36,129S), and C62S,C129S (C62,129S)), or triple cysteine mutant (C36S,C62S,C129S (C36,62,129S)) were homogenized in lysis buffer with 0.5% Triton X-100. The soluble and insoluble fractions were isolated, and 3 or 30 μl of the extracts, respectively, were analyzed by Western blotting. B, densitometry analysis of blots expressed as the ratio of immunoreactivity of AKAP79-YFP over flotillin (loading control). Data are presented as mean ± S.E. for four independent experiments; **, p < 0.01 (compared with wild type), #, p < 0.01 between indicated groups. n.s., not significant. C, cells expressing AKAP79-YFP wild type or the cysteine mutants indicated were treated with azide-palmitate for 24 h and then lysed in RIPA buffer, and AKAP79-YFP was immunoprecipitated. The azide-palmitate incorporated in AKAP79 was biotinylated by reaction with alkyne-biotin and detected by streptavidin-HRP blotting. The right-hand blot confirms expression of AKAP79 constructs in all samples. Data are representative of three similar experiments.