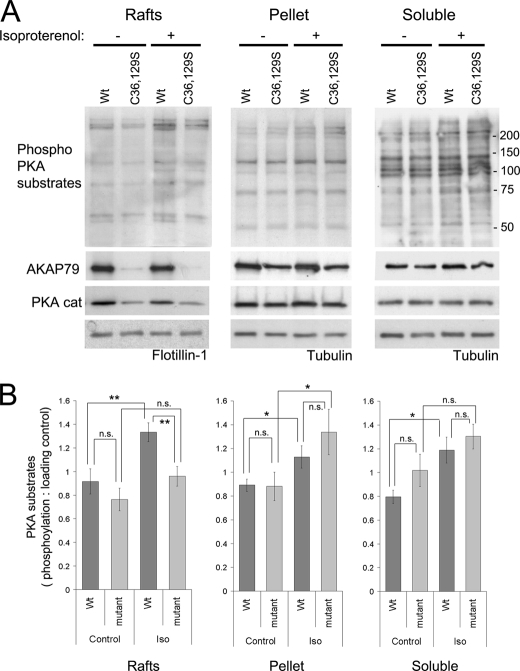
FIGURE 6.
Recruitment of PKA to lipid rafts by AKAP79 allows the phosphorylation of substrates following β-adrenergic receptor stimulation. A, HEK-293 cells stably expressing AKAP79-YFP wild type and the double mutant (C36S,C129S (C36,129S)) were stimulated with isoproterenol (10 μm for 4 min at 37 °C), washed with cold PBS, and homogenized with Tris-HCl buffer with 0.5% Triton X-100. Soluble and insoluble extracts were isolated, and the insoluble extracts were loaded on density gradients. The resultant light fractions (2 and 3; lipid rafts) were pooled and centrifuged to precipitate proteins. The raft fractions, the pellet of the gradient, and the soluble extracts were analyzed by Western blot to detect the phosphorylation of PKA substrates and the presence of AKAP79 and PKA catalytic subunits (PKA cat). Flotillin-1 and tubulin were used as loading controls. B, densitometry analysis of blots (taking into account all the proteins detected by the antibody) with the phospho-PKA substrate antibody corrected against loading control (mean ± S.E.), for two independent experiments with cells expressing the double mutant (C36S,C129S) and three experiments with cells expressing the triple mutant (C36S,C62S,C129S) of AKAP79, **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. Iso, isoproterenol; n.s., not significant.