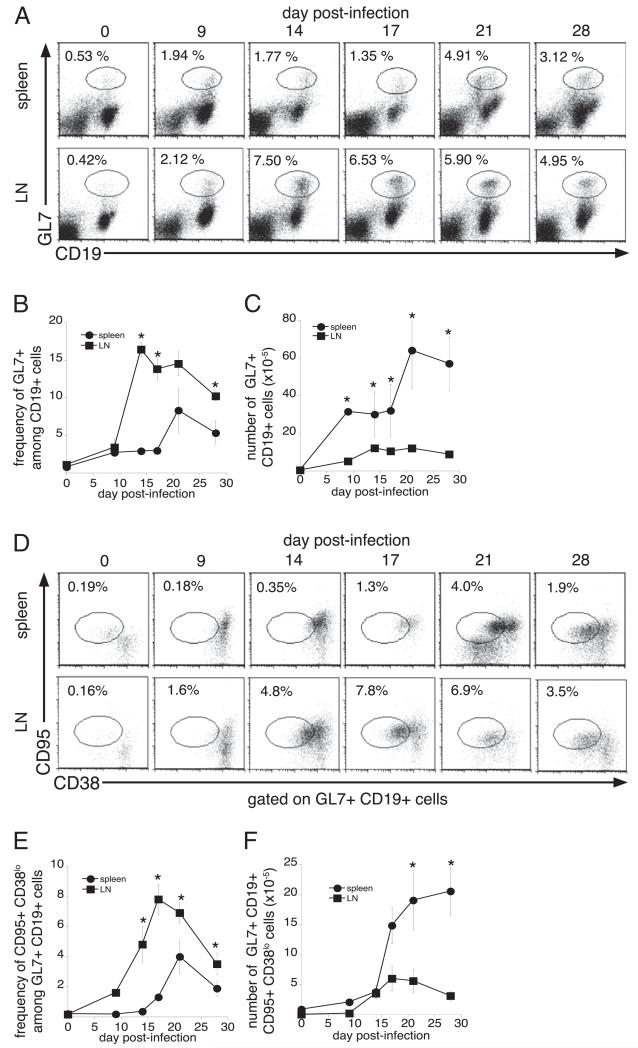
FIGURE 3.
Infection inhibits the differentiation of splenic GC B cells. A, To determine the kinetics of the onset of the GC response, cells from the spleen (top row) and lymph nodes (bottom row) of C57BL/6 mice were stained with Abs directed against GL7 and CD19, on the indicated days postinfection. The frequencies (B) and numbers (C) of GL7-positive B cells are shown. D, To further characterize GC B cells, the GL7+ CD19+ cells were analyzed for their expression of CD38 and CD95. The frequencies and numbers of GC B cells (i.e., CD95+CD38lo cells), within the GL7−, CD19-positive flow cytometry gate, are shown in E and F. The data are representative of three independent experiments in which three mice were analyzed at each time point. *p ≤ 0.05.