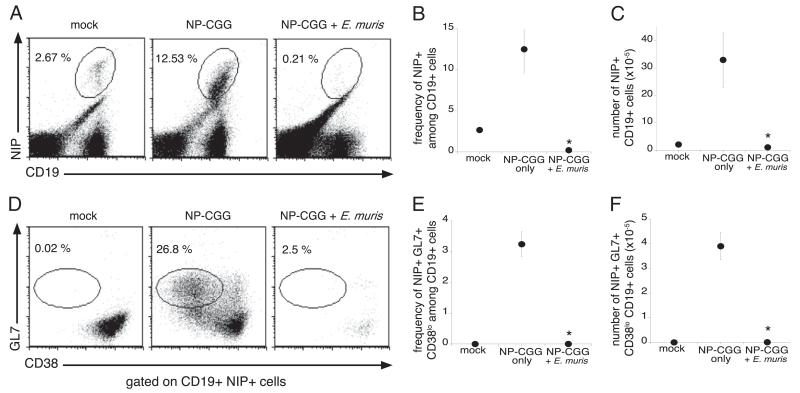
FIGURE 6.
The differentiation of spleen GC B cells was suppressed during infection. On day 2 after E. muris infection, infected (m+s)Ig B cell transgenic mice and mock-infected mice were immunized with NP-CGG and analyzed 12 d later. A, Splenocytes were stained for cell surface expression of NIP and CD19, to detect Ag-specific B cells. The frequencies of NIP-specific B cells among the total B cells (B) and the numbers of Ag-specific B cells (C) were determined. D, The NIP+ CD19+ B cells were analyzed for cell surface expression of GL7 and CD38 to identify GC B cells. The frequencies (E) and numbers (F) of GC B cells among the total CD19-positive B cells were determined. The data are representative of three independent experiments in which three mice were analyzed at each time point. *p ≤ 0.05.