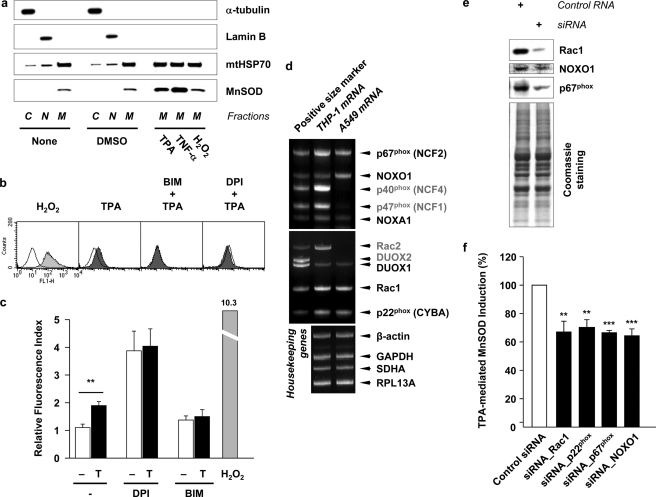
FIGURE 1.
Superoxide radical anion generated by NADPH oxidase in response to TPA induces MnSOD in mitochondria. a, A549 cells were fractionated into cytosolic (C, α-tubulin as a marker), nuclear (N, LaminB as a marker), and mitochondrial (M, mtHSP70 as a marker) fractions after treatment of TPA (32.4 nm, (20 ng/ml)), TNF-α (10 ng/ml) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (1 mm) for 24 h at 37 °C. Each fraction sample was separated using 10–20% Tris-glycine gel and analyzed by immunoblotting. b, after incubation with either PKC inhibitor BIM (1 μm) or NADPH oxidase inhibitor DPI (100 nm) for 1 h, cells were treated with TPA for 30 min. The cells were further incubated in the presence of 40 μm 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) for 30 min at 37 °C. Stained cells were washed with PBS and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACS). H2O2 (1 mm) was treated as a positive control. c, DCF fluorescence index was presented as a ratio to the cells not exposed to both inhibitors and TPA (T). Values are means ± S.E. (n ≥ 4, **, p < 0.01). d, components of NADPH oxidase in A549 cells are examined by dual priming oligonucleotide (DPO) PCR system (missing components in A549 cells are presented as gray letters). For the data in e and f, small interfering RNA (siRNA) for Rac1, p22phox, p67phox, and NOXO1 (250 nm each) were used to knockdown each components of NADPH oxidase, which exist in A549 cells. Sixty hours after transfection of siRNAs, cells were treated with TPA for additional 24 h at 37 °C. e, Western blots for Rac1, NOXO1 and p67phox after knockdown by each siRNAs. Coomassie-stained gel shows that equal amounts of sample were loaded. f, inhibitory effect of siRNAs on the TPA-mediated MnSOD induction was presented as a percentage to the MnSOD induction in cells transfected with control siRNA and treated with TPA. Values are means ± S.E. (n ≥ 3, **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001 versus control siRNA by ANOVA; n.s., not significant).