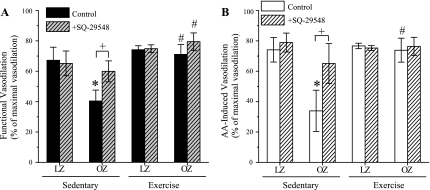
Fig. 3.
The effect of exercise training on functional and AA-induced vasodilation in the cremaster muscle. A: OZ exhibited significantly blunted functional vasodilation compared with LZ in the Sed group (*P = 0.01, two-way ANOVA). Chronic exercise training significantly enhanced functional vasodilatory response in OZ (#P = 0.006, two-way ANOVA). SQ-29548 pretreatment significantly enhanced functional vasodilation vs. OZ control (+ P = 0.003, two-way RM ANOVA). SQ-29548 had no effect on vasodilation in Sed LZ, Ex OZ, or LZ induced by functional stimulation compared with the control group. B: AA-induced vasodilations are similar to the results of functional vasodilation. *Significant difference vs. LZ Sed (P = 0.003, two-way ANOVA). #Significant difference vs. OZ Sed (P = 0.003, two-way ANOVA). SQ-29548 has a similar effect on AA-induced vasodilation as on functional vasodilation. Values are means ± SE (LZ Sed, n = 6; OZ Sed, n = 5; LZ Ex, n = 6; OZ Ex, n = 5).