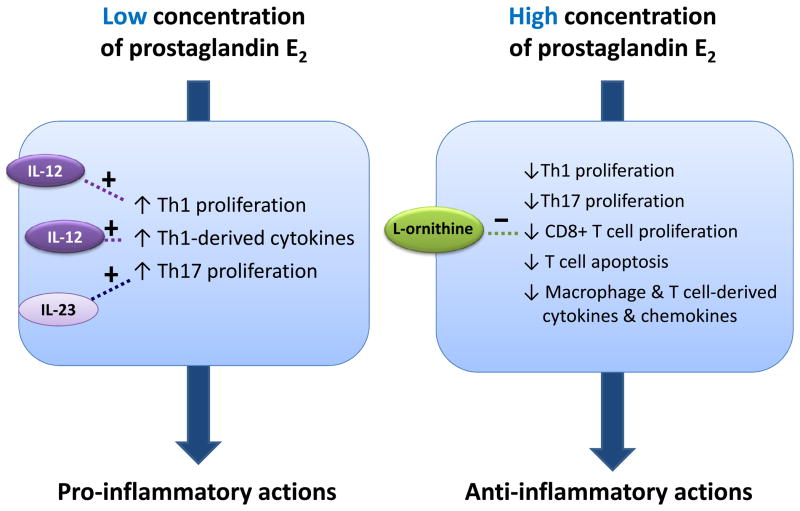
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the proposed bi-modal effect of prostaglandin E2. In the presence of certain modulators, such as IL-12 or IL-23, a low concentration of prostaglandin E2 results in pro-inflammatory signals. Conversely, a high concentration of prostaglandin E2 leads to anti-inflammatory responses. Modulators such as L-ornithine decrease proliferation of CD8+ T cells, thereby preventing anti-inflammatory action.