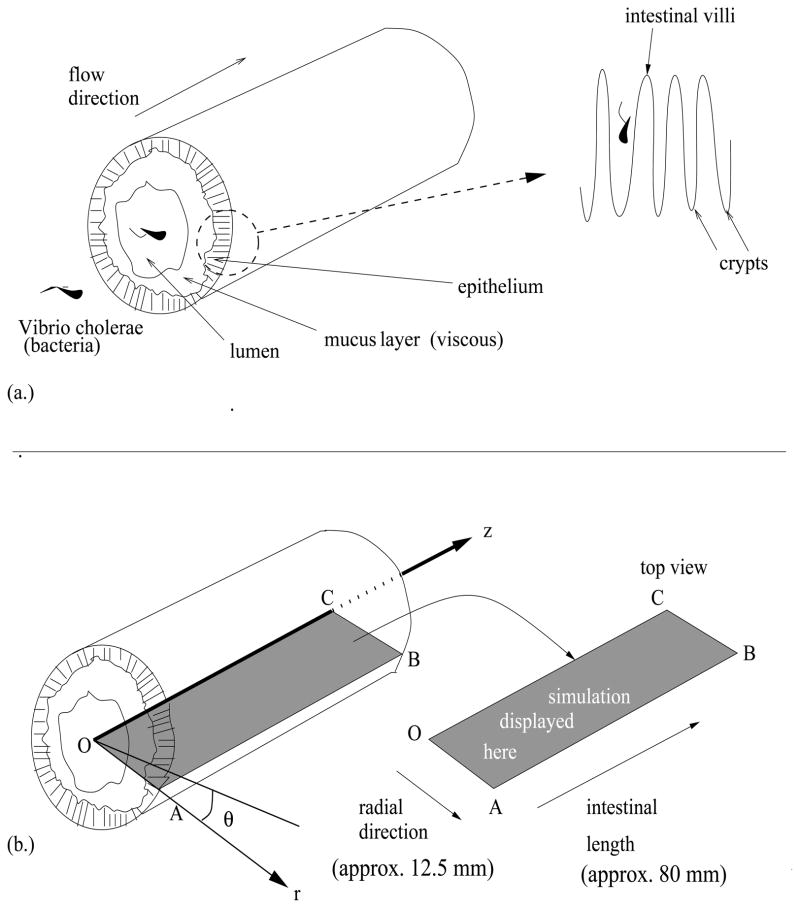
Figure 1.
(a.) Small intestinal section. A 3-dimensional cross-section of the intestine including the detailed structure of the epithelium, which is composed of villi and crypts. (b.) Mathematical framework. The mathematical description of the intestinal cross-section in terms of the coordinates r, z, and θ,. The left is the three-dimensional illustration of an intestinal cross section. The rectangular slice OABC is the display platform for our simulations (see Figure 2). The line segment OC represents the line through the center of the lumen, and AB represents the outer edge of the intestinal wall. The three-dimensional result is visualized using radial symmetry of the intestinal section. See [54].