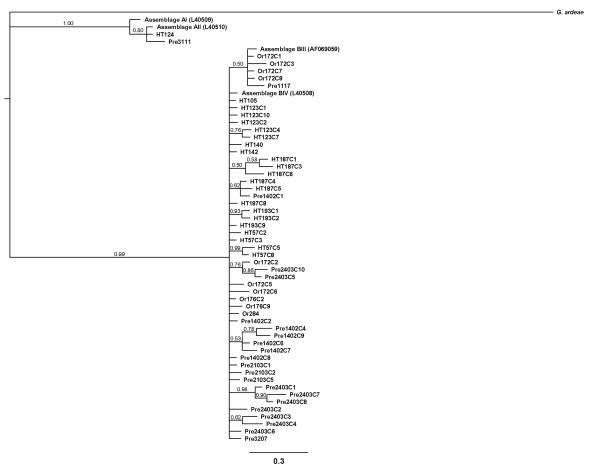
Figure 1.
Bayesian analyses of the gdh gene were performed using the HKY85+Γ+I, selected by jModelTest version 0.1 [42], as a model of sequence evolution. Starting trees were random, four simultaneous Markov chains were run for 1,000,000 generations, and trees were sampled every 100 generations. Bayesian posterior probabilities were calculated using a Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling approach implemented in MrBAYES program. The sequence HT124 is 100% identical to HT137, HT144, Or006, Or019, Or87, Or88, Or94, Or98, Or140, Or215, Or262, Or287, Pre1209, Pre2208, TSH292, TSH408, TSH1123, and TSH2014. The sequence HT105 is 100% identical to HT187C2, Or176C1, Pre016, Pre1402C5, Pre2018, Pre2103C3, and TSH1250. The sequence HT123C1 is 100% identical to TSH1210. The sequence HT142 is 100% identical to HT57C1. The sequence HT187C5 is 100% identical to HT193C8 and Pre2320. The sequence HT187C8 is 100% identical to Or172C4. The sequence Pre2103C1 is 100% identical to TSH090 and TSH1119. Posterior probabilities < 0.50 are omitted.