Figure 1.
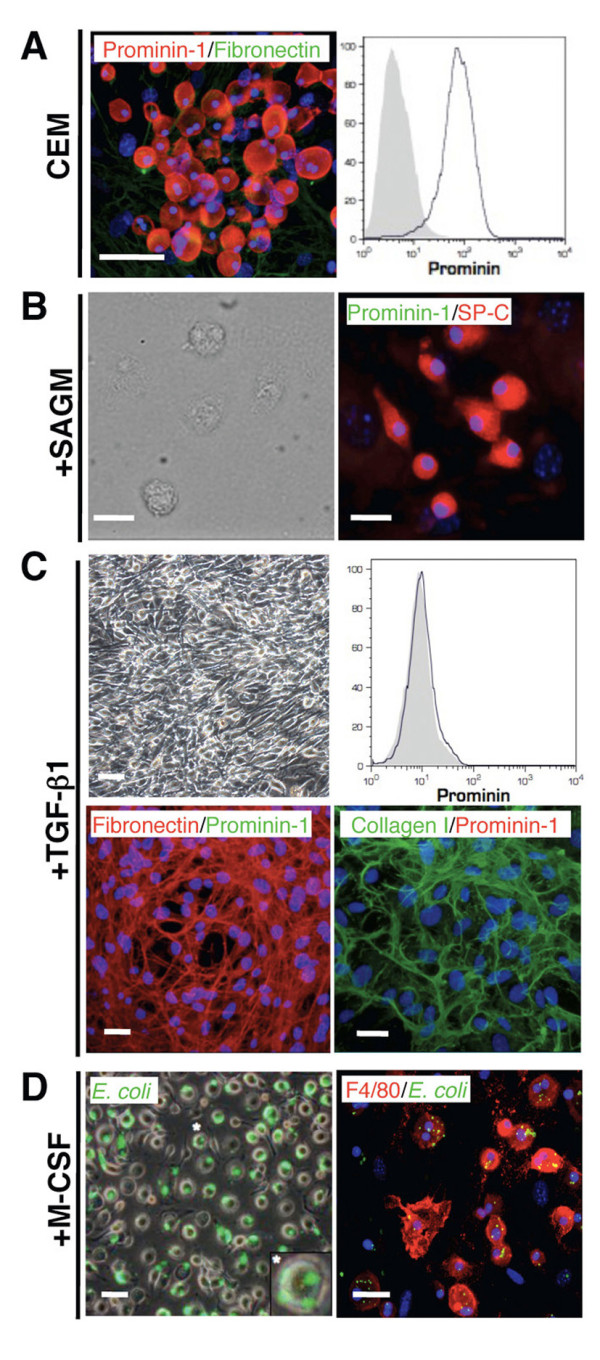
Lung-derived prominin-1+ cells turn into alveolar type II epithelial cells, fibroblasts or macrophages after exposure to different cytokines and growth factors. Expansion of cells from the healthy lung explants in the culture expansion medium (CEM) resulted in round, semi-adherent prominin-1-positive cells and fibronectin-positive feeder layer (A, left). Harvested cells contained mostly prominin-1-positive cells (A, right). Further, prominin-1-positive cells were isolated using magnetic cell sorting and cultured in the presence of different cytokines and growth factors. Prominin-1+ cells cultured in the Small Airway Growth Medium (SAGM) for 14 days became surfactant protein-C (SP-C)-positive and prominin-1-negative (B). Prominin-1+ cells cultured in the presence of TGF-β for 14 days lost prominin-1 expression, but instead produced fibronectin and collagen I (C). Exposure of prominin-1+ cells to M-CSF for 7 days resulted in formation of E.coli phagocytising F4/80-positive cells (D). DAPI visualized cell nuclei. Bars = 20 μm.
