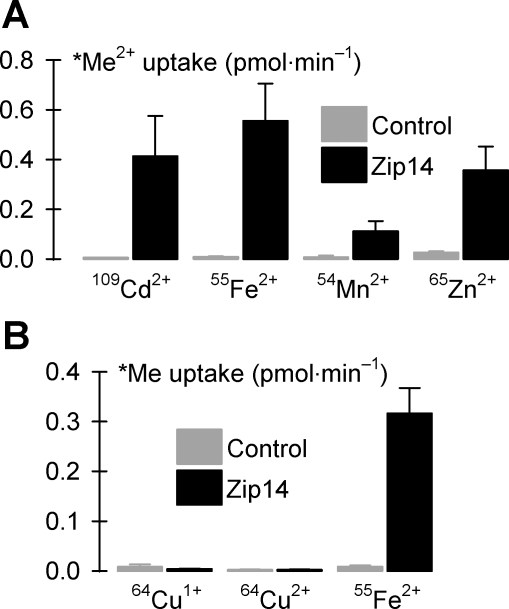
Fig. 7.
Metal-ion substrate profile of Zip14. A: uptake of radionuclide metal ions (*Me2+, each at 2 μM in the presence of 1 mM l-ascorbic acid) in control oocytes and oocytes expressing Zip14 (n = 17–27). Two-way ANOVA revealed an interaction (P < 0.001); for all metals, Zip14 differed from control (unadjusted P < 0.001); within Zip14, all metals differed from one another (109Cd2+ vs. 65Zn2+, unadjusted P = 0.039; all other pairwise comparisons, unadjusted P < 0.001). B: uptake of 2 μM 64Cu was measured in the presence of 1 mM l-histidine and in the presence (64Cu1+) or absence (64Cu2+) of 1 mM l-ascorbic acid and compared with uptake of 2 μM 55Fe2+ in the presence of 1 mM l-ascorbic acid in control oocytes and oocytes expressing Zip14 (n = 13–15). Two-way ANOVA revealed an interaction (P < 0.001); Zip14 did not differ from control for 64Cu1+ (P = 1.0) or 64Cu2+ (P = 0.56) but differed for 55Fe2+ (P < 0.001).