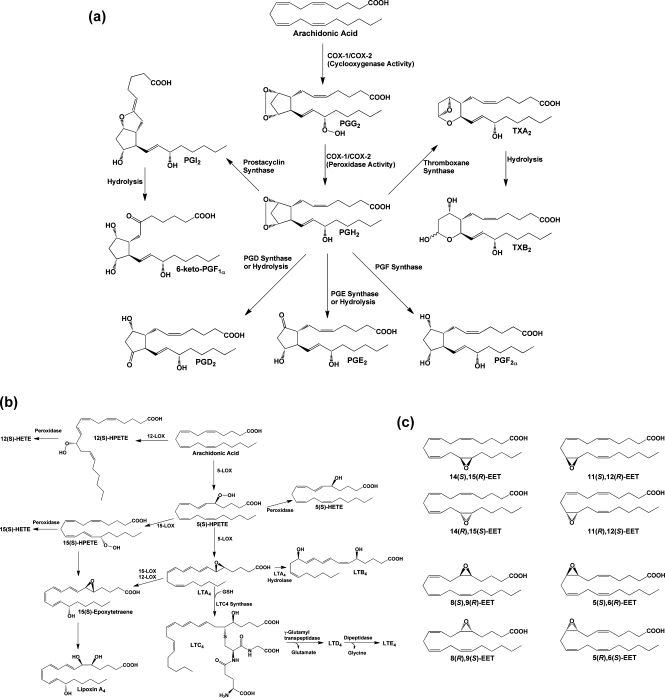
Figure 1.
(a) Cyclooxygenase pathway of AA metabolism. AA is converted to PGG2 at the cyclooxygenase active site of COX-1 or COX-2 and is then reduced to PGH2 at the peroxidase active site. PGH2 spontaneously decomposes to yield PGE2 or PGD2, but these compounds, as well as PGF2α, PGI2, and TxA2, are also produced enzymatically by specific synthases. PGI2 and TXA2 are unstable and spontaneously decompose to yield 6-keto-PGF1α and TXB2, respectively. The ethanolamide and glyceryl ester of PGH2 produced from the metabolism of AEA and 2-AG, respectively, are converted to the same range of eicosanoid products as PGH2 with the exception of the TXA2 analogue. (b) Lipoxygenase pathway of AA metabolism. AA is converted by LOX enzymes to position-specific HPETEs, which are then reduced to the corresponding HETEs. 5-LOX also converts 5-HPETE to LTA4, which may then be metabolized to LTB4 or LTC4. The glutathionyl moiety of LTC4 is subject to enzymatic hydrolysis, yielding LTD4 and LTE4. The actions of multiple LOX enzymes lead to the formation of lipoxins. An example is provided for the synthesis of lipoxin A4 through multiple steps catalyzed by 5-LOX and either 15-LOX or 12-LOX. (c) Cytochromes P450 catalyze the epoxygenation of AA at each of the double bonds, producing the range of products shown.