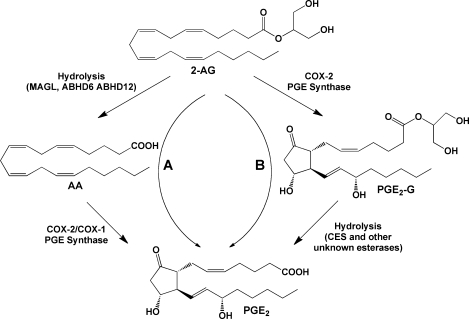
Figure 11.
Hydrolytic metabolism of 2-AG and PG-Gs. Pathway A: 2-AG may be hydrolyzed to AA, which is then subject to oxygenation by COX-2 or COX-1, yielding free acid PGs (illustrated here by PGE2). Pathway B: Oxygenation of 2-AG will produce PG-Gs (illustrated here by PGE2-G), hydrolysis of which will yield the corresponding free acid PG. The origin of the free acid PG product, through oxygenation of AA or 2-AG, cannot readily be distinguished.