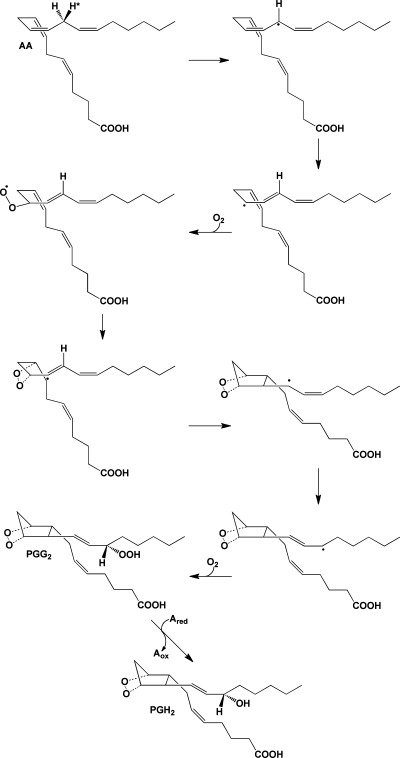
Figure 5.
Mechanism of the cyclooxygenase reaction. The 13-pro-(S)-hydrogen of AA is removed by a radical at Y385 of the COX active site. The resulting radical migrates to position 11, which serves as the site of oxygen addition. Following the formation of the endoperoxide between carbons 11 and 9, a single bond links carbons 8 and 12 to form the prostanoid five-membered ring. The radical then migrates to carbon 15, which becomes the site of the second oxygen addition, forming a peroxyl radical, which is then reduced to a hydroperoxide (PGG2). Reduction of the 15-hydroperoxide using electrons from a coreductant (Ared) at the peroxidase active site yields PGH2.