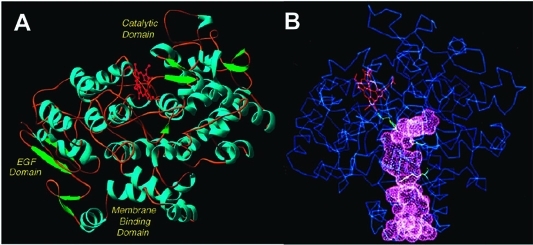
Figure 7.
(A) Domain structure of the COX enzymes. The N-terminus (not visible in the crystal structure) connects to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) domain. The EGF domain, in turn, connects to the membrane-binding domain, which comprises four α-helices (A–D). Helix D connects the membrane-binding domain to the large catalytic domain. α-helices are shown in blue, β-sheets are shown in green, and the heme prosthetic group is shown in red. (B) Drawing of the COX structure highlighting the hydrophobic channel of the cyclooxygenase active site. The large lobby region, which opens into the membrane-binding domain, is separated from the L-shaped channel above by a constriction. Key catalytic residues Tyr-385, Arg-120, and Ser-530 are shown in green. The heme prosthetic group is in red. These structural characteristics shown here for ovine COX-1 are representative of both isoforms. Panel B kindly provided by M. Garavito. Both figures reprinted from ref (44). Copyright 2003 American Chemical Society.