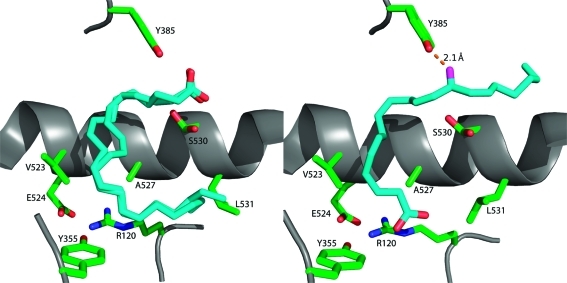
Figure 8.
Comparison of the conformations of AA in the active sites of the two monomers of murine COX-2. The left frame displays AA bound in monomer A of the COX-2 homodimer. It is bound in an inverted catalytically unproductive conformation in which its carboxyl group is H-bonded to Tyr-385 and Ser-530. The ω end of the fatty acid lies across Arg-120 and abuts Leu-531. Two molecules of AA are modeled in monomer A because of ambiguities in modeling from the electron density map. The right frame displays AA bound in monomer B of the homodimer in a productive conformation. The carboxylate is H-bonded to Arg-120, and the fatty acid chain projects up into the active site. The ω end of the fatty acid projects into an alcove above Ser-530, and the 13-pro-(S) hydrogen is located adjacent to the hydroxyl group of Tyr-385, which is converted to a tyrosyl radical during turnover.