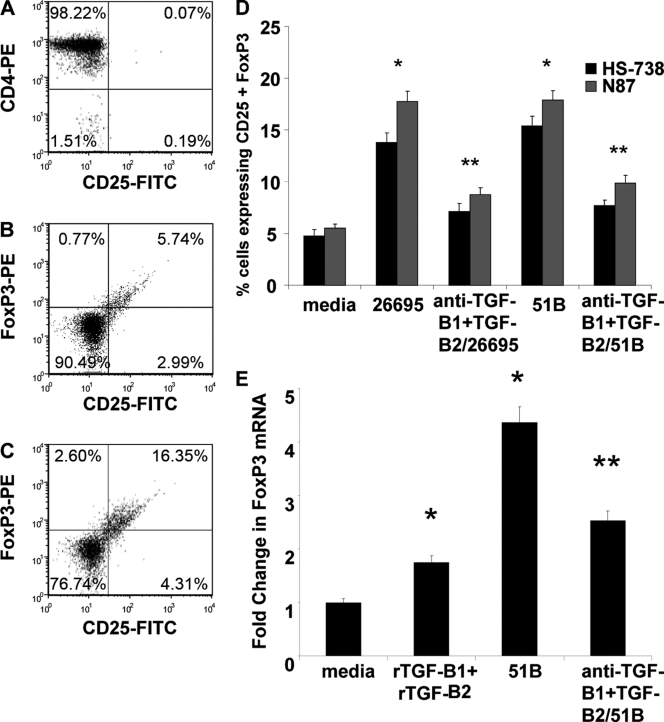
Fig. 6.
H. pylori-induced GEC-derived TGF-β promotes resting naïve CD4+ T cell development into CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Naïve CD4+ T cells isolated by negative selection were stained with anti-CD4 antibodies to assess purity (A). Isolated cells were cocultured with GECs (B) or GECs (C) exposed to H. pylori and stained for CD25 and FoxP3 in representative dot plots. (D) Compiled data for CD25 and FoxP3 staining of CD4 T cells from cultures with untreated cells, H. pylori-exposed cells, and H. pylori-exposed cells with anti-TGF-β1 and anti-TGF-β2 neutralizing antibodies. (E) FoxP3 mRNA levels were also examined by quantitative real-time PCR. Results indicate fold changes over the level for the isotype control relative to the level for the 18S housekeeping gene. Data shown are means ± SEM of results from 4 experiments, each performed in duplicate (n = 8). *, P < 0.05 for comparison to untreated cells; **, P < 0.05 for comparison to H. pylori-treated cells.