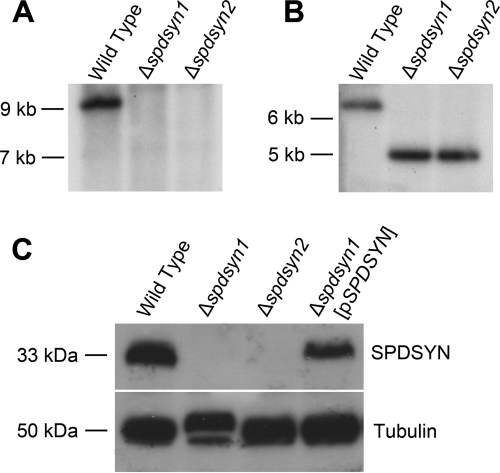
Fig. 1.
(A and B) Molecular characterization of the SPDSYN locus and SPDSYN expression in the Δspdsyn knockouts. Two micrograms of genomic DNA from wild-type, Δspdsyn1, or Δspdsyn2 parasites was digested with SalI and hybridized to a 1.0-kb fragment of the SPDSYN coding region (A) or XhoI and hybridized to a 1.2-kb fragment of the 5′ flanking region (B). Molecular size markers are indicated, and equal loading of DNA was verified via ethidium bromide staining. (C) For protein expression analysis, protein lysates from 1.0 × 106 wild-type, Δspdsyn1, Δspdsyn2, and Δspdsyn1(pXG-BSD-SPDSYN) [Δspdsyn1(pSPDSYN)] promastigotes were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with polyclonal antibodies against L. donovani SPDSYN. Tubulin expression was analyzed as a loading control.