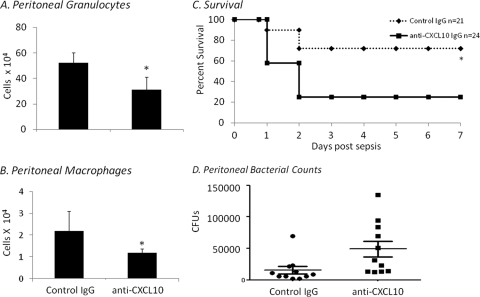
Fig. 4.
CXCL10 blockade worsens survival and cell recruitment. Two hours prior to sepsis (LD40), neonates were administered either anti-CXCL10 IgG (squares and solid line) or control IgG (0.5 mg; diamonds and hashed line). Peritoneal washes were harvested from neonates administered anti-CXCL10 or control IgG at 12 h postsepsis. Cells were subsequently stained for granulocytes (Gr-1+ CD11b+) (A) and macrophages (F4/80+ CD11b+) (B) and analyzed by flow cytometry. The figure represents the summary of two experiments. Values represent the mean ± SDs (n = 6 each; *, Student's t test, P < 0.05; error bars indicate SDs). (C) Another cohort of animals was then monitored for survival for 7 days. The figure represents the summary of three experiments (n = 45; *, Fisher's exact test, P < 0.003). (D) Peritoneal bacterial counts were determined following sepsis in neonates that were administered either control IgG or anti-CXCL10 (n = 11 per group; values represent the mean ± SDs; *, Student's t test, P = 0.026).