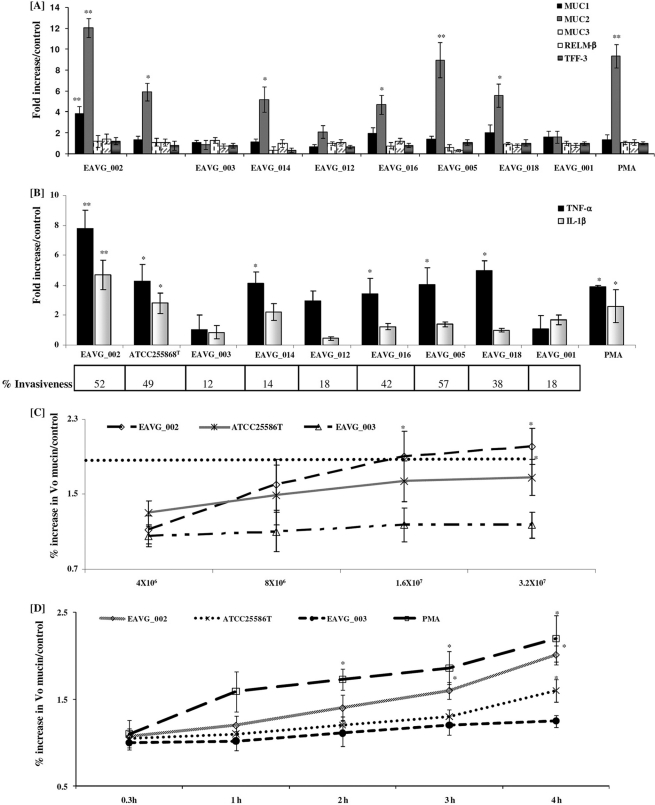
Fig. 1.
F. nucleatum infection induces mucin and proinflammatory cytokine gene expression in LS 174T colonic cells. (A) Effects of F. nucleatum isolates on MUC1 to -3 gene expression and goblet cell innate defense mediators. (B) Effects of F. nucleatum isolates and PMA on proinflammatory cytokine gene expression. The percent invasiveness into Caco-2 cells was determined using immunofluorescence microscopy and was calculated as (number of invaded cells in a field of view)/(total number of cells in the same field) × 100 (see Materials and Methods for details). (C) Concentration-dependent effect of F. nucleatum infection on the release of high-molecular-weight mucin (S4B V0 mucin/controls; see Materials and Methods for details) after 4 h. The dotted horizontal line represents the fold increase in mucin gene expression induced by the positive control PMA. (D) Time-dependent increase in high-molecular-weight V0 mucin secretion by F. nucleatum isolates (1.6 × 107 CFU/ml). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.