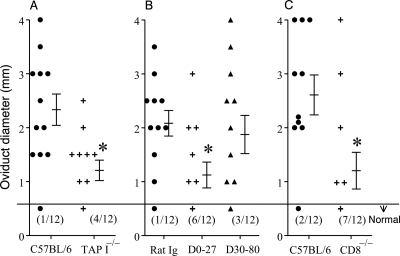
Fig. 3.
Role of CD8+ T cells in oviduct sequelae after vaginal C. muridarum infection. Groups (n = 6) of mice (C57BL/6 and TAP I−/− [A], control rat Ig and anti-CD8 antibody treated [B], and C57BL/6 and CD8−/− [C]) were challenged with 5 × 104 IFU of C. muridarum on day 0, and the macroscopic oviduct diameter was measured on day 80 after challenge. Each individual marker represents one oviduct, and the mean ± SEM of oviduct diameter per group of mice also is shown. The number of normal oviducts (numerator) and the total number of oviducts evaluated (denominator) per respective group of mice have been indicated in parentheses. *, significant (P ≤ 0.05, Student's t test) difference in oviduct diameter between the indicated group and C57BL/6 mice in panels A and C or control rat Ig-treated mice in panel B). In panels B and C, * indicates significant (P ≤ 0.05, chi-square test) difference in oviduct diameter between the indicated group and control rat Ig-treated mice or C57BL/6 mice, respectively. Results are representative of three independent experiments.