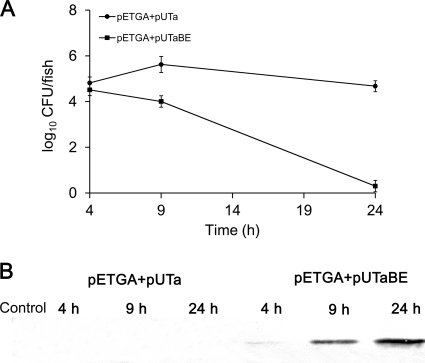
Fig. 5.
Cell lysis and antigen release in vivo in zebrafish. After intraperitoneal injection with 5 μl of PBS, E. coli BL21(DE3)/pETGA+pUTa (107 CFU per fish), or E. coli BL21(DE3)/pETGA+pUTaBE (107 CFU/fish), 20 fish with similar weights from each group were randomly taken at 4, 9, and 24 h postinjection. The tissues surrounding and including the abdominal cavities were collected, and the weight of each sample was kept at between 6 and 7 g. The tissue samples were then homogenized in 15 ml PBS. (A) Bacterial survival in zebrafish. Each homogenate sample was diluted serially in PBS and plated in triplicate on LB agar containing kanamycin and ampicillin to count the CFU. (B) Antigen release by bacterial cells in zebrafish. Each homogenate sample, collected at defined time intervals, was centrifuged to harvest the supernatant, and the concentrated supernatant was analyzed by Western blotting to detect the antigen GAPDH.