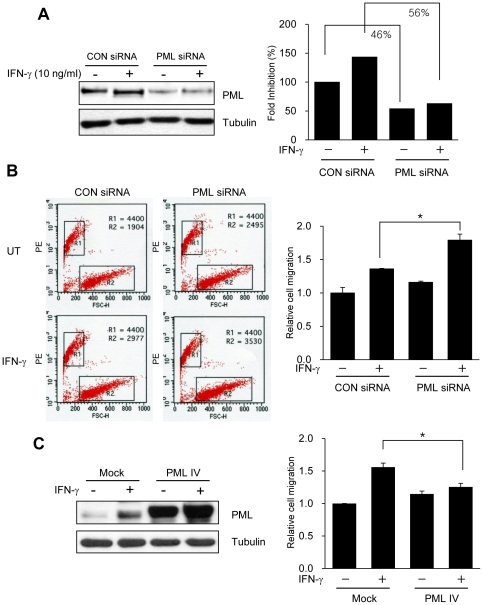
Figure 2. Reduced PML Protein Expression by siRNA Increases T-cell Infiltration/Migration.
(A) SNU-638 gastric cancer cells were transiently transfected with Pml siRNA or control siRNA. Two days after transfection, cells were treated with or without interferon-gamma (IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 8 h and lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting. Effective siRNA-mediated suppression of PML protein expression was verified for each assay by immunoblotting. (B) Jurkat cells and culture supernatants from SNU-638 cells which were transiently transfected with either control siRNA or Pml siRNA were analyzed by a transwell migration assay. After transfection, SNU-638 cells were incubated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 8 h or left untreated, and the collected supernatants were placed in the lower chambers. The upper chambers received 5×105 Jurkat cells in a volume of 100 µl and the transwell migration units were incubated at 37°C for 2 h. Migration of Jurkat cells from the upper to lower chamber was analyzed by examining cells harvested from the lower chambers by fluorescent count-bead mediated counting on a flow cytometer. Relative cell migration was determined by the number of migrated cells normalized to the number of cells migrating to supernatants from SNU-638 cells transiently transfected with control siRNA without IFN-γ, and the value from parental cells was arbitrarily set at 1. (C) SNU-638 gastric cancer cells were transiently transfected with either empty vector (Mock) or PML IV expression vector (PML IV). Day after transfection, cells were treated with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 8 h and culture supernatants were obtained and subjected to transwell migration assay as described in B. PML protein expression was verified for each assay by immunoblotting. Data shown are representative of at least three experiments. Bars, SD. *P<0.05.