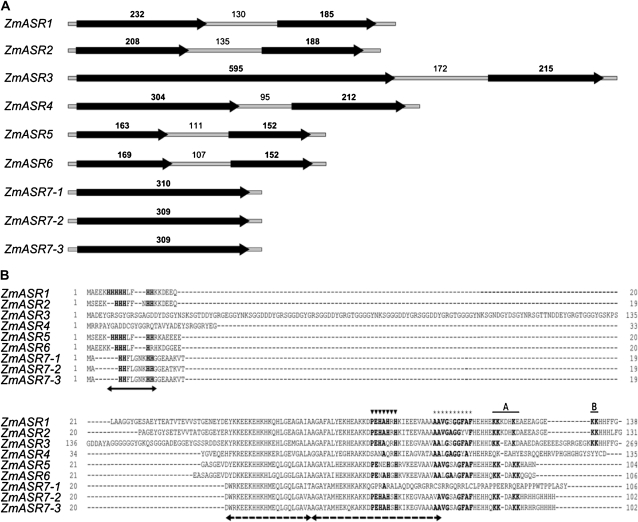
Figure 1.
Gene structure of ZmASR genes. A, Schematic drawing of the exon/intron structure of ZmASR genes. Black arrows and thin gray bars indicate exons (boldface numbers) and introns (lightface numbers), respectively, the sizes of which are in bp. B, Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of ZmASR genes. Arrows denote the two highly conserved regions of ASR proteins: a small N-terminal consensus of approximately 18 to 20 amino acids containing a stretch of six His residues (solid arrow) and a large C-terminal region containing two ABA/WDS signatures (dashed arrows). Amino acid positions determined to be the Zn2+-dependent DNA-binding activity domain and a sequence possibly hindering DNA binding of the SlASR1 protein (Rom et al., 2006) are marked with triangles and stars, respectively. Amino acid positions determined to be the A and B regions of the bipartite nuclear localization signal of the LLA23 protein (Wang et al., 2005) are overlined. Amino acids identical to LLA23 or SlASR1 proteins are shown in boldface.