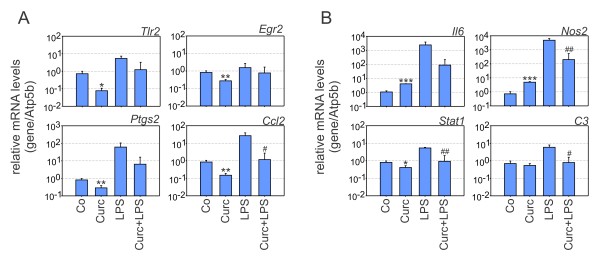
Figure 3.
Curcumin potently blocks pro-inflammatory gene expression. Real-time qRT-PCR validation of transcripts in BV-2 microglia stimulated with 20 μM curcumin, 100 ng/ml LPS, or 20 μM curcumin + 100 ng/ml LPS for 6 hours. Relative mRNA levels were quantified for (A) Toll-like receptor 2 (Tlr2), Early growth response 2 (Egr2), Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 (Ptgs2), Chemokine ligand 2 (Ccl2), and (B) Interleukin 6 (Il6), Nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2, alias iNos), Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (Stat1), Complement C3 (C3). Expression was normalized to the control gene Atp5b and mRNA levels (+/- SD) are graphed relative to control cells. Results are calculated from three independent experiments performed in triplicate measurements. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001 for curcumin vs. control, and # p ≤ 0.05, ## p ≤ 0.01 for curcumin + LPS vs. LPS, Mann-Whitney Rank Sum test.