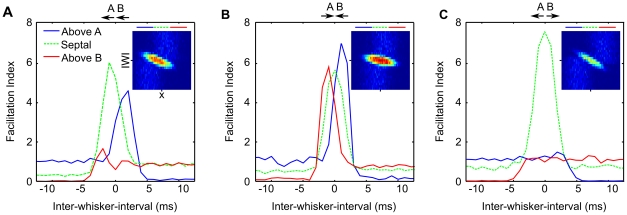
Figure 8. Direction-specific interactions.
There is evidence that leftward or rightward deflections of the principal whisker tend to excite L4 neurons situated on the left or the right of the barrel respectively. Therefore to simulate the expected effect of deflecting the whiskers in different directions, we offset the center of activity in the model L4 by  . A As in ref. [18] both whiskers were deflected to the left, as indicated by the pairs of arrows above each plot. The relationship between inter-whisker-interval and neuron location is the same but shifted for increasing intervals to neurons closer to barrel A. The resulting asymmetry is of the same form as that in Figure 1, increasing the secondary peak in above A neurons, decreasing that in the above B group, and shifting the septal group interval tuning negatively. B If the whiskers are deflected toward each other, intra-cortical distances are effectively shortened and the model predicts that facilitatory interactions will be distributed more evenly across L2/3. C Conversely if the whiskers are deflected away from each other, distances are increased and all facilitatory interactions are confined to the septal region. The conditions represented in panels B and C have not yet been conducted experimentally and could therefore be used to falsify the model.
. A As in ref. [18] both whiskers were deflected to the left, as indicated by the pairs of arrows above each plot. The relationship between inter-whisker-interval and neuron location is the same but shifted for increasing intervals to neurons closer to barrel A. The resulting asymmetry is of the same form as that in Figure 1, increasing the secondary peak in above A neurons, decreasing that in the above B group, and shifting the septal group interval tuning negatively. B If the whiskers are deflected toward each other, intra-cortical distances are effectively shortened and the model predicts that facilitatory interactions will be distributed more evenly across L2/3. C Conversely if the whiskers are deflected away from each other, distances are increased and all facilitatory interactions are confined to the septal region. The conditions represented in panels B and C have not yet been conducted experimentally and could therefore be used to falsify the model.