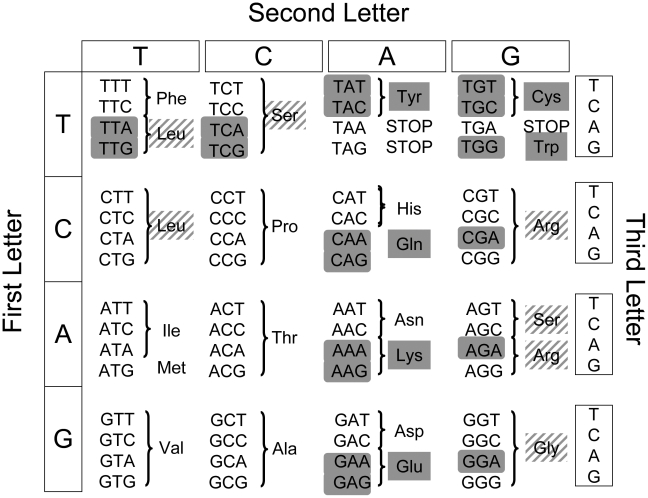
Figure 1. Sense codons differ in their propensity for conversion to STOP codons.
The Standard Genetic Code contains 18 fragile codons (shaded) that can be changed into a STOP codon by a single point-mutation and whose mistranscription can therefore generate nonsense errors. The remaining 43 sense codons are “robust” to such errors. Six amino acids are encoded exclusively by fragile codons (“fragile amino acids”, shaded), ten amino acids are encoded exclusively by robust codons (“robust amino acids”, unshaded) and four amino acids can be encoded either by robust or fragile codons (“facultative amino acids”, hatched shading).