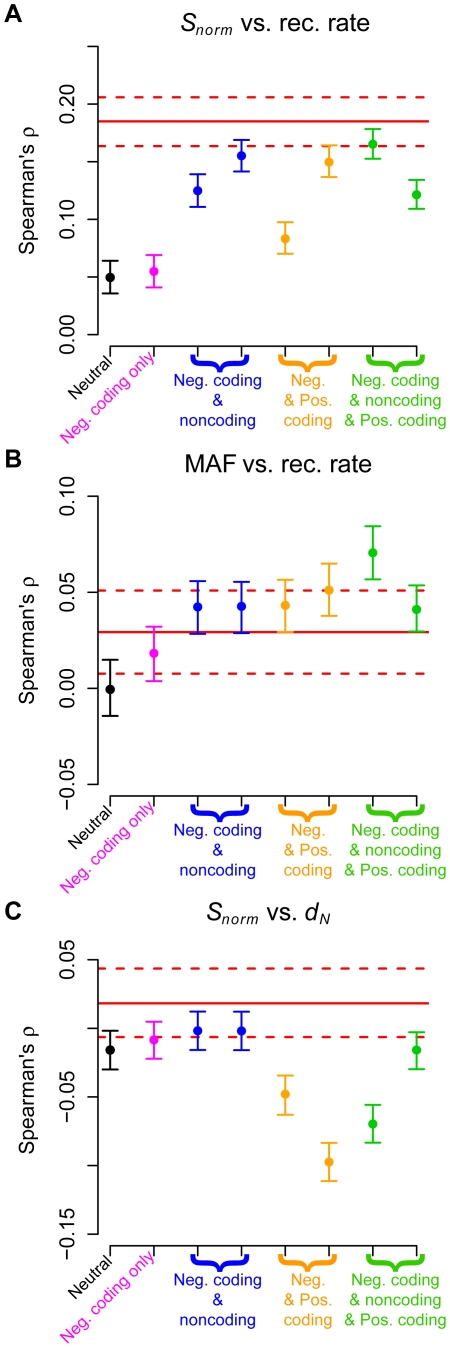
Figure 2. Comparison of Spearman's  for genic regions with the expected values based on forward simulations for the low-coverage dataset.
for genic regions with the expected values based on forward simulations for the low-coverage dataset.
(A) Number of SNPs per covered base divided by human-chimp divergence (Snorm) versus recombination rate. (B) Average minor allele frequency versus recombination rate. (C) Number of SNPs per covered base divided by human-chimp divergence (Snorm) versus human-chimp nonsynonymous divergence (dN). The red solid lines denote the point estimates from the genic regions in the low-coverage data. The dotted lines represent 95% confidence intervals obtained by bootstrapping. Black points denote a model with no selection and pink points a model where negative selection acted only on nonsynonymous mutations. Blue points denote models where both nonsynonymous and some intronic sites were subjected to negative selection. Orange points denote models where most nonsynonymous mutations were negatively selected, but some were positively selected. Green points denote models where nonsynonymous and some intronic mutations were subjected to negative selection, but a fraction of nonsynonymous mutations were positively selected. See Table S6 for a more detailed description of the different models of selection. Nonsynonymous divergence was measured from the simulations as the fraction of differences between the human and chimp sequences at first and second codon positions.