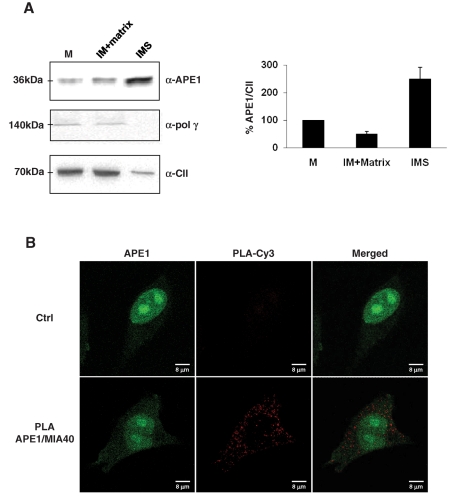
FIGURE 6:
Mitochondrial APE1 is accumulated within the IMS of mitochondria and interacts in vivo with the mitochondrial IMS import and assembly protein 40 (Mia40). (A) Mitochondria from bovine hearth were fractionated with digitonin and subsequent differential centrifugation to separate matrix and IMS, which are compartments rich in soluble proteins. Sixty micrograms of total mitochondrial extract (M), matrix plus inner membrane fraction (IM), and intermembrane space (IMS) fraction alone was separated onto 12% SDS–PAGE and then blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, which was further immunoblotted with anti-APE1, anti–Poly γ, and anti–complex II (α-CII) antibodies. Western blotting analysis showed that only the full-length protein was present within the mitochondrial fractions, and APE1 was predominantly found in the IMS fraction rich of soluble proteins. Polymerase γ, used as marker of non–freely soluble matrix protein of the mitochondrial BER system, was confirmed to be associated with the inner membrane–containing particulate fraction. Total mitochondria extracts were used as a positive control; complex II was used as a marker of the inner membrane. Average percentage values of APE1 normalized for CII ± SD of three independent experiments are plotted in the relative histogram (right) of Western blot analysis (left). (B) PLA technology was used to demonstrate the occurrence of the interaction between APE1 and Mia40. PLA reaction was performed following manufacturer's instructions. Confocal microscopy analysis highlighted the presence of distinct fluorescent red dots (PLA signals) indicating the occurrence of in vivo interaction between APE1 and Mia40; green fluorescence shows the APE1 localization within the cell. Negative control is represented by cells incubated only with α-APE1 antibody.