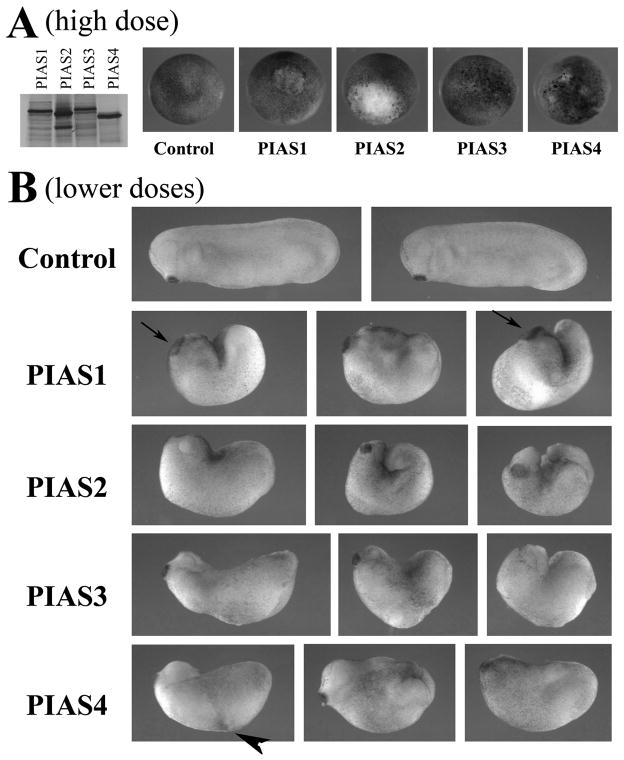
Figure 3. Ectopic expression of PIAS genes in early frog embryos disrupts Xenopus development.
A) In vitro translation showed that all PIAS proteins were synthesized efficiently from their cognate RNAs. When RNAs were injected at high doses (2ng), PIAS1, 2 and 4 induced severe lesions in embryos at early gastrula stages and embryonic lethality before tailbud stages. PIAS3 was less effective in inducing the lesions. B) When the doses of the RNAs were adjusted to allow embryo survival (shown here were embryos injected with RNAs of 1ng PIAS1, 0.5ng PIAS2, 2ng PIAS3 and 1ng PIAS4), the resulting tailbud embryos showed failure in blastopore closure, shortened body axis, and defective head formation. The embryos with ectopic PIAS1 often displayed enlarged cement gland (arrows), and the embryos with elevated PIAS4 sometimes formed pigmented aggregates at the flank (arrowhead).