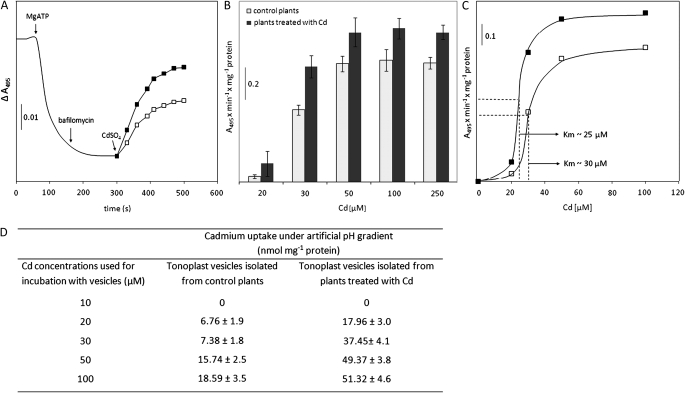
Fig. 5.
The properties of Cd transport into tonoplast vesicles imposing an electrochemical proton gradient. (A) Effect of 30 μM CdSO4 on the proton gradient generated by V-ATPase in tonoplasts isolated from control plants (open squares) and plants treated with Cd (filled squares). (B) Effect of different Cd concentrations on acridine orange absorbance change measured in vesicles imposing a ΔpH generated by V-ATPase. (C) Cd concentration dependence of Cd transport into tonoplast vesicles isolated from control (open squares) and Cd-treated (filled squares) plants with Km values given. (D) The average net uptake of Cd for vesicles imposing an artificial pH gradient and subjected to direct vacuum filtration and AAS analyses. The values of Cd uptake were corrected for the amount of metals unspecifically bound to tonoplasts measured in control conditions without a pH gradient (data not shown). The presented values are representative of the results obtained in 3–4 independent experiments with each experiment done in triplicate (B–D) except for A which presents values corresponding to a representative experiment of at least four independent assays.