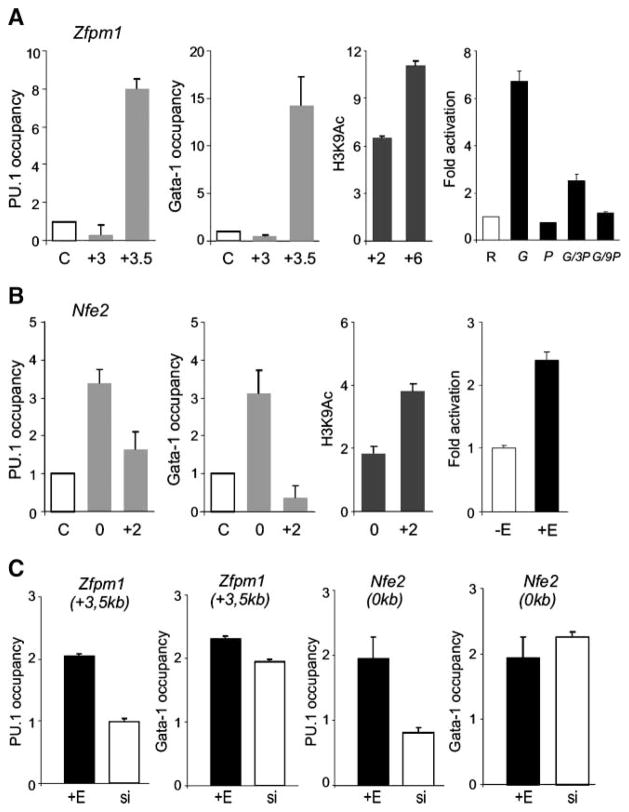
FIGURE 5.
Colocalization of GATA-1 and PU.1 proteins near Zfpm1 and Nfe2 genes and chromatin H3K9 hyperacetylation induced by ectopic GATA-1 activation. ChIP was carried out on cross-linked chromatin as described in Materials and Methods and in the legend to Fig. 4. Antibodies used were anti-PU.1, anti–GATA-1 (gray columns), anti–acetylated histone H3K9 (black columns), and antirabbit IgG antibody (letter C on the X-axis). A and B. Occupancy of PU.1 and GATA-1 proteins at the indicated positions (relative to transcription start site, in kilo-bases) near Zfpm1 and Nfe2 was determined in unstimulated MELGER cells. Levels of H3K9 hyperacetylation in these cells in the presence of 10−7 mol/L of 17β-estradiol for 24 h (third graphs) was determined relative to acetylation determined in stimulated MELPUER cells under the same conditions. Primary binding sites of GATA-1 are functional in reporter assays. A. Right, HeLa cells were transfected with reporter plasmid [Zfpm1, 0.25 μg (R)] and cDNA constructs [pXM-GATA-1, 0.125 μg (G) and pXM-PU.1, 0.125 μg (P); 0.375 μg (3P); 1.125 μg (9P)]. B. Right, MELGER cells were lipofected with Nfe2 reporter plasmid (1.7 μg) and either un-stimulated (−E) or further stimulated with 17β-estradiol after 24 h (+E) followed by measurement of luciferase activity at 72 h (for details, see Materials and Methods). C. MELPUER cells were either stimulated with 17β-estradiol (+E) or treated with PU.1-inhibiting siRNAs (si) for 48 h, and GATA-1 and PU.1 occupancy was detected by qChIP near Nfe2 (0 kb) and Zfpm1 (+3.5 kb) genes. All ChIP bars in C indicate the fold change (Y-axis) of DNA fragment in specific immunoprecipitates above the immunoprecipitates using control antirabbit IgG antibody. Bars, SE of at least two independent experiments.