Figure 2.
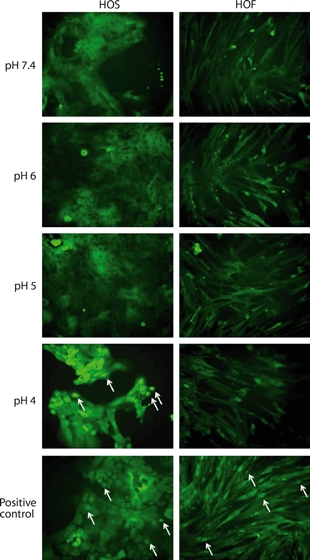
Immunohistochemical localization of NF-κB after exposure of cells to acid. Human oesophageal squamous (HOS) and human oesophageal fibroblasts (HOF) cells were exposed to pH 7.4, pH 6, pH 5 or pH 4 medium for 30 min. lipopolysaccharide-treated positive control cells (2-h treatment) are also shown. Positive control HOS and HOF cells and pH 4 exposed HOS cells show nuclear localization of NF-κB (arrows). Following all other treatments, NF-κB is detected in the cytoplasm, demonstrating no NF-κB activation. The HOF cells at pH 4 show an abnormal morphology and reduced adhesion, which can be attributed to a reduction in cell viability.
