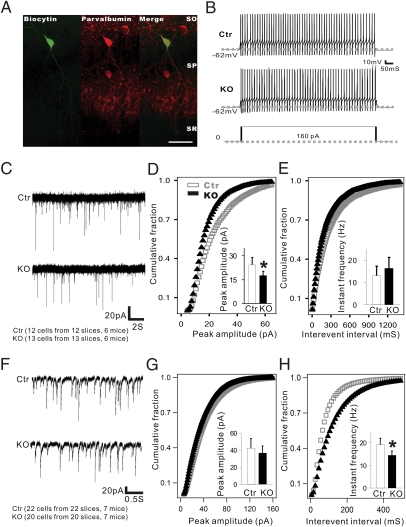
Fig. 4.
Reduced mEPSC amplitude in PV+ interneurons and mIPSC frequency in pyramidal cells in TrkB-PV−/− (KO) mice. (A) Double immunohistochemistry of biocytin-labeled and recorded fast-spiking PV+ interneurons in the CA1 region. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (B) Fast repetitive firing from the labeled cells from Ctr and KO mice. Action potentials were evoked by a 160-pA depolarizing current injected into neurons in the current clamp recording configuration. No differences in the excitability of fast-spiking cells were observed between Ctr and KO mice. (C) Sample traces of mEPSCs in fast-spiking neurons recorded from Ctr and KO mice. (D and E) Cumulative probability distributions were plotted against mEPSC amplitude and interevent interval in the fast-spiking neurons of Ctr and KO mice. The amplitude distribution of mEPSCs in mutant mice showed a left shift compared with control mice, indicating a reduction of mEPSCs amplitude in mutant mice. (F–H) Summary of mEPSCs amplitude and frequency was shown in both Ctr and KO mice, respectively. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05.