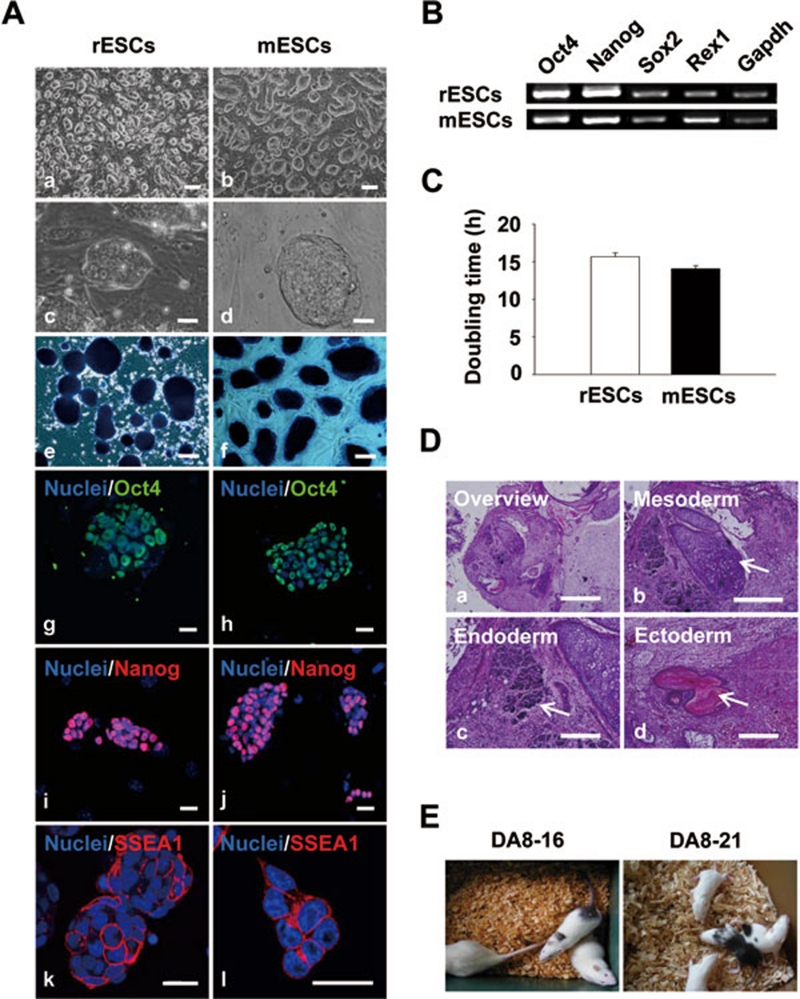
Figure 1.
Characteristics of rESCs maintained in 2i conditions. (A) Undifferentiated rESCs (a, c, e, g, i, k) and mESCs (b, d, f, h, j, l). (a-d) Phase contrast images show undifferentiated rESC and mESC colonies on mitotically inactivated MEFs. (e, f) Colonies were positive for ALP staining. (g-l) Colonies were immunopositive for pluripotency markers Oct4 (g, h), Nanog (i, j), and SSEA-1 (k, l). Scale bars = 200 μm (a, b), 100 μm (e, f), and 20 μm (c, d, g-l). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). (B) RT-PCR analysis of pluripotency marker expressions in rESCs compared with mESCs. Gapdh indicates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, housekeeping gene. (C) Comparison of doubling time between rESCs and mESCs; n = 3. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of histological sections of teratoma derived from rESC line DA8-16. Teratoma (a) was composed of various types of tissue: cartilage (mesoderm, b), primitive renal cells (endoderm, c), and pigmentary epithelium (ectoderm, d). Scale bars = 1 mm (a), 500 μm (b), and 200 μm (c, d). (E) Generation of live adult coat-color chimeras from both the established rESC lines. Agouti coat-color indicates the donor rESCs of DA strain. MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; rESCs, rat embryonic stem cells; mESCs, mouse embryonic stem cells.