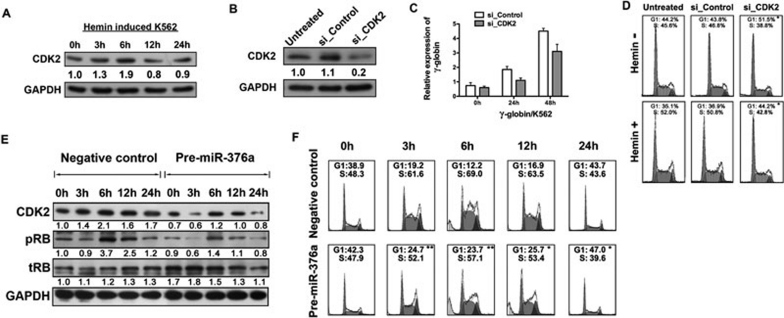
Figure 5.
MiR-376a inhibits erythroid proliferation by targeting CDK2 in early erythroid differentiation. (A) Immunoblotting of CDK2 in extracts from K562 cells that were induced with hemin for 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. GAPDH serves as a loading control. (B) Immunoblotting of CDK2 and GAPDH in extracts of K562 cells 48 h after transfection with a control siRNA (si_Control) or a siRNA for CDK2 (si_CDK2). The results showed a decrease in CDK2 expression in the cells transfected with si_CDK2. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of γ-globin expression in K562 cells induced by hemin for 24 and 48 h after si_Control or si_CDK2 transfection. Comparative real-time PCR was performed in triplicate and the expression level of γ-globin was normalized to GAPDH mRNA. Error bars represent standard deviation. (D) Cell cycle analysis of K562 cells that are un-induced or induced by hemin for 24 h after 24 h cell transfection with si_Control or si_CDK2. Inhibitory S phases are seen in the si_CDK-transfected cell cycle image. (E) Immunoblotting of CDK2, phosphorylated RB, total RB, and GAPDH in extracts from K562 cells induced by hemin for 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after cell transfection with pre-miR-376a or the negative control. The signal in each lane was quantified using ImageJ software and the ratio of CDK2, pRB, and tRB to GAPDH was determined. (F) Cell cycle analysis of K562 cells that are un-induced or induced by hemin for 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after cell transfection with pre-miR-376a or the negative control. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.