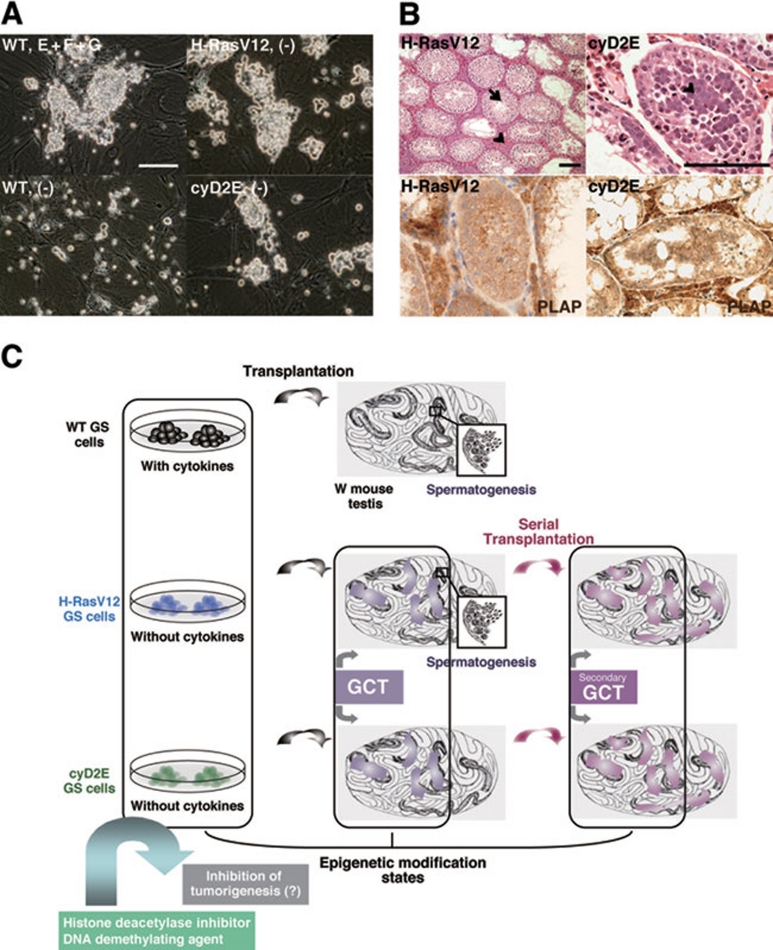
Figure 2.
SSC self-renewal in vitro and tumorigenesis by Ras-cyclin D2 activation. (A) H-RasV12- and cyclin D2/E (cyD2E)-transfected GS cells can proliferate in the absence of growth factors, while WT GS cells cannot be cultured in the absence of growth factors. (B) Development of germ cell tumors (GCTs) in recipient testes of H-RasV12- and cyD2E-transfected GS cells (top). Although abnormal undifferentiated spermatogonia proliferation was detected in both recipients, the observation of both spermatogenesis (arrow) and interstitial tumor infiltration (arrowhead) was made only in H-RasV12-GS cell recipients. Secondary GCTs were developed by serial transplantation for both H-RasV12-GS and cyD2E-GS cells and these GCTs expressed PLAP, the marker of seminomatous tumors (bottom). (C) Schemes of an antitumor strategy in mouse. Based on our findings, H-RasV12-GS and cyD2E-GS cells may show different epigenetic modifications (DNA methylations or histone modifications) compared to WT GS cells. Further, it might be possible to detect some differences in testicular cells between WT GS recipients and H-RasV12-GS and cyD2E-GS recipients containing GCTs and secondary GCTs. Altering epigenetic marks (states) through the addition of histone deacetylase inhibitor and DNA demethylating agent into H-RasV12-GS and cyD2E-GS cells might be able to inhibit tumorigenesis. Bars, 100 μm.