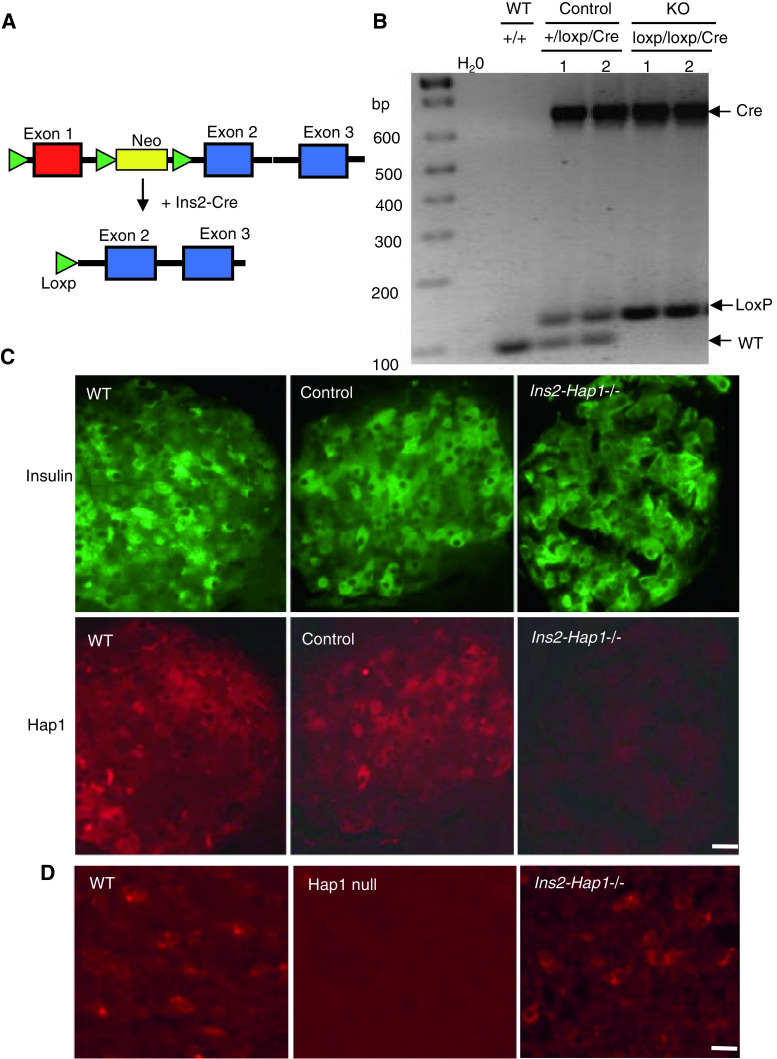
Fig. 1.
Generation of conditional Hap1 knockout mice that deplete Hap1 in pancreatic β-cells. a Exon1 of the mouse Hap1 gene was flanked by loxP sites in the targeted allele. Mice carrying this targeted gene were mated with transgenic mice that express Cre in pancreatic β-cells driven by the mouse preproinsulin 2 (Ins2) promoter, resulting in offspring mice that have exon1 of the Hap1 gene deleted. b PCR genotyping of crossed mice showing the presence of the Cre and loxP alleles in two homozygous loxp/loxp/Cre and two heterozygous (+/loxp/Cre) mice, but not in wild-type (+/+) mice. For simplicity, homozygous loxp/loxp/Cre mice are referred to as Ins2-Hap1−/− or KO, and heterozygous (+/loxp/Cre) as Ins2-Hap1± or control. c Double immunofluorescence staining of insulin (green) and Hap1 (red) showing Hap1 depletion in insulin-positive β-cells in KO mice. d Immunofluroescent Hap1 staining of the hypothalamic tissues of Ins2-Hap1−/− and WT mice at the age of 2 months. The hypothalamus of Hap1 germline knockout pup (Hap1 null) at postnatal day 1 served as a control to show the specific labeling of Hap1 by the anti-Hap1 antibody. Scale bars 10 μm