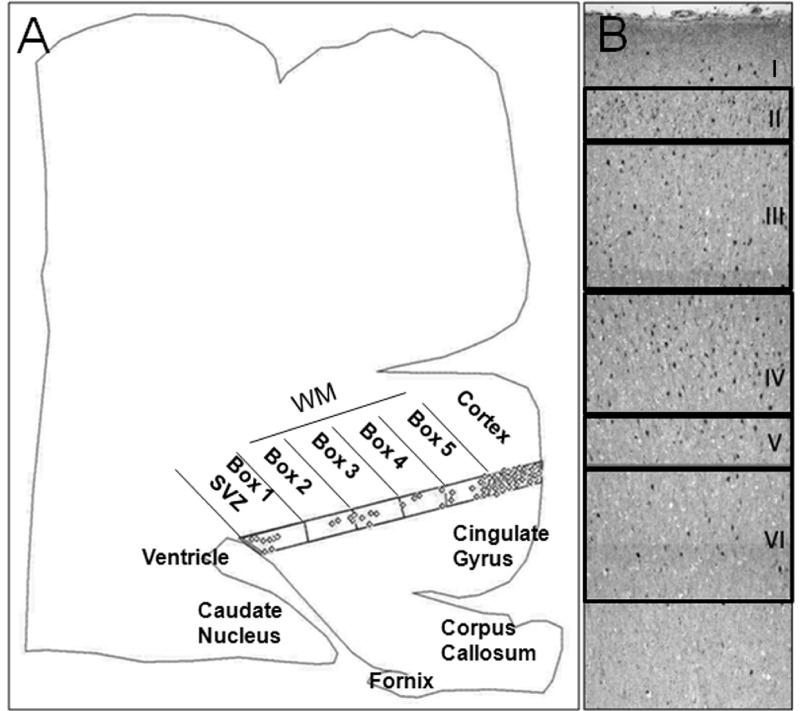
Figure 1.
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic) cell counting methods. (A) A computer-generated plot from a tracing of a tissue section of cerebral cortex in a term infant shows the distribution of GABAergic neurons in the ventricular/subventricular zone (SVZ), periventricular, deep, and central white matter (WM) and overlying cerebral cortex. The SVZ, WM and subplate region is equally divided into 5 boxes by an overlying grid: Box 1 is located at the SVZ; Box 5 is located directly underneath Layer VI (subplate proper), with the periventricular, deep, and central WM in the intervening boxes. GABAergic neuron density in each box is obtained by dividing neuronal number by box area. (B) A low-power view demonstrates the subdivisions of the cerebral cortex for counting in a tissue section immunostained for glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65/67). The cortex is divided into 6 boxes according to the individual cytoarchitectonic layers.