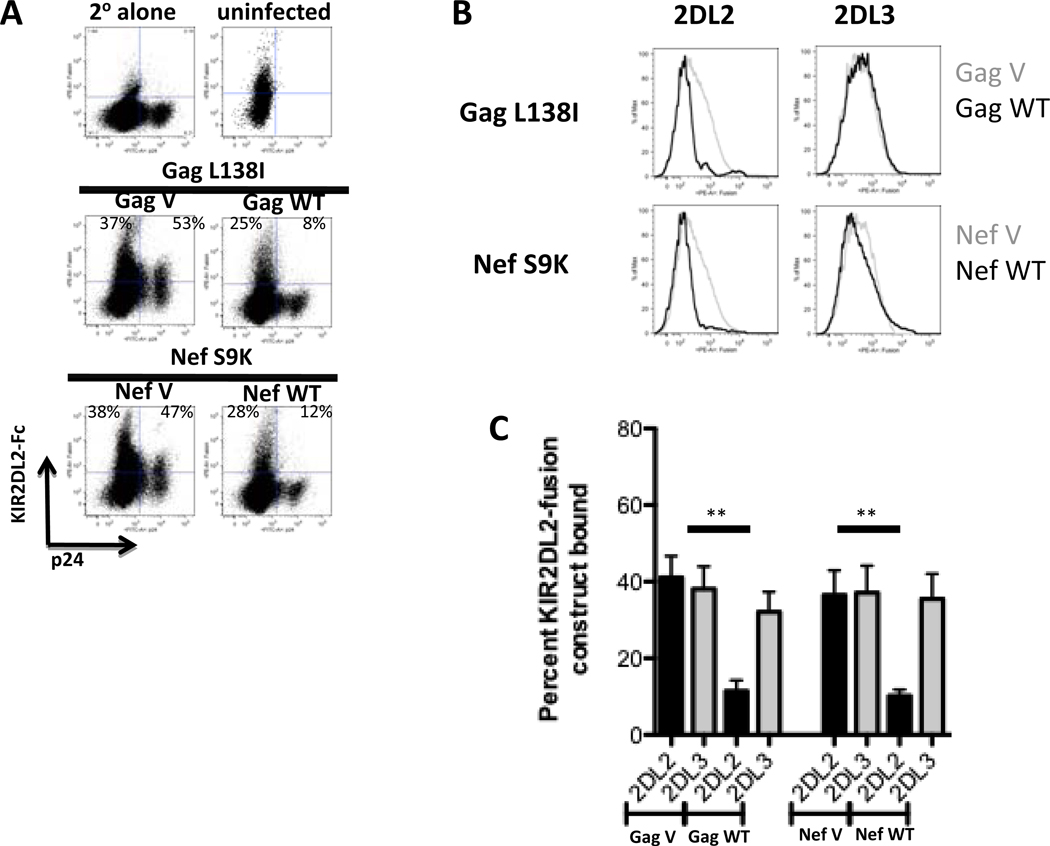
Figure 4. KIR2DL2-associated amino acid polymorphisms affect KIR2DL2-, but not KIR2DL3-binding to infected CD4+ T cells.
CD4+ T cells infected with the respective variant viruses were stained with KIR2DL2-IgG and KIR2DL3-IgG fusion constructs. The dot plots (A) and histograms (B) depict the staining pattern of KIR2DL2-IgG and KIR2DL3-IgG fusion constructs of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells from a HLA-C1/C2 heterozygous donor. The bar graph summarizes KIR2DL2- (black) or KIR2DL3- (grey) IgG fusion construct binding data for 5 different HLA-C1/C2 heterozygous CD4+ T cell donors for the viral variants, as indicated (C). ** p < 0.005