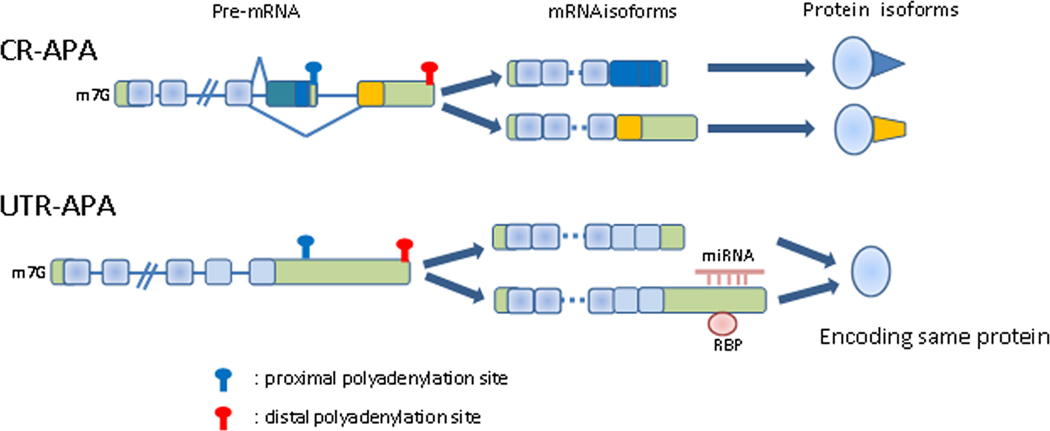
Figure 1. Schematic representation of CR-APA and UTR-APA.
CR-APA produces mRNA isoforms with distinct C-terminal coding regions, resulting in distinct protein isoforms. UTR-APA produces distinct mRNA isoforms with different length 3’UTRs, but encode the same protein. Longer 3’UTRs usually contain cis-regulatory elements, such as miRNA and/or protein binding sites, which often bring about mRNA instability or translational repression. CR-APA, coding region-alternative polyadenylation; UTR-APA, 3’UTR-alternative polyadenylation. Light green boxes, untranslated regions; blue light blue boxes, shared coding regions; dark blue and yellow boxes, unshared coding regions; lines, introns.