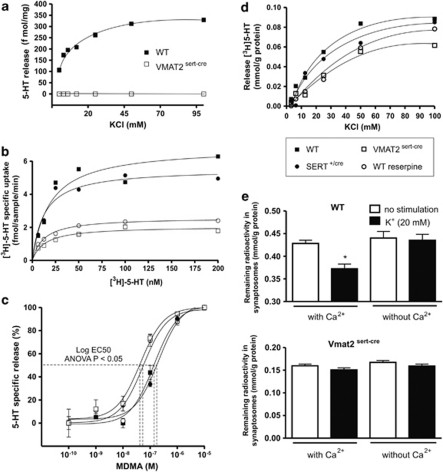
Figure 4.
Uptake and release of [3H]-5-HT using synaptosome preparations obtained from whole brain in controls, SERTcre/+, and VMAT2sert−cre mice. (a) The release of endogenous 5-HT evoked with varying concentrations of potassium in synaptosomes from WT mice was not observed in synaptosomes from VMAT2sert−cre mice (n=3). (b) [3H]5-HT uptake in VMAT2sert−cre or reserpine-treated (0.1 μM) synaptosomes compared with WT or SERTcre/+ synaptosomes. There was less total uptake in synaptosomes from VMAT2sert−cre mice or from WT mice treated with the VMAT inhibitor reserpine (Vmax; VMAT2sert−cre=2.0±0.1 fmol/min, reserpine=2.6±0.07, mean±SEM, n=3) compared with synaptosomes from WT or SERTcre/+ mice (Vmax: control=6.8±0.5 fmol/min; SERTcre/+=5.5±0.3, n=3). There were no significant changes (using one-way ANOVA) in the Km values between groups (WT=18.8±4.5 nM; VMAT2sert−cre=13.5±3.2 nM; SERTcre/+=12.7±3 nM; reserpine=12.25±1.4 nM; means±SEM, n=3). (c) The concentration response curve of the MDMA-induced [3H]5-HT release was slightly shifted to the left in preloaded synaptosomes from VMAT2sert−cre mice or reserpine-treated synaptosomes. (d) There were no major changes in potassium-induced [3H]5-HT release between various synaptosome preparations in conditions weakly dependent on calcium, n=3. (e) Under conditions in which potassium-induced release is fully dependent on the presence of calcium in the incubation buffer (brief stimulation in the absence of pargyline, WT synaptosomes top panel) there was no significant release in preloaded synaptosomes from VMAT2sert−cre mice (bottom panel).