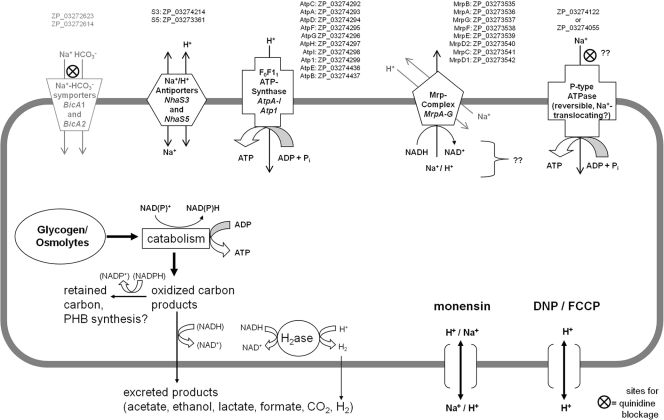
Fig. 7.
Proposed mechanisms involving sodium and proton gradients and ATP production and hydrolysis in A. maxima. Each circled X indicates a site where quinidine is likely to block the influx of sodium. The ionophore monensin collapses sodium gradients across cell membranes by exchanges with protons. DNP and FCCP are proton ionophores that collapse proton gradients. NCBI reference sequences of putative membrane proteins (possibly) involved in proton-sodium gradient utilization are given from the draft genome sequence of A. maxima. Sodium bicarbonate symporters are likely present but probably do not play a role in catabolism of carbohydrates during autofermentation. That protein representation is therefore shown in gray.