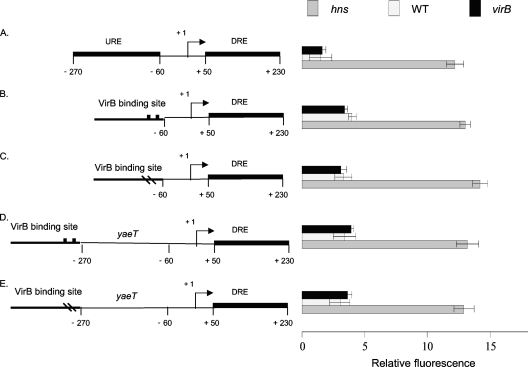
Fig. 4.
The URE and VirB-dependent proU derepression. Summaries of the structures of various derivatives of the E. coli proU promoter region are presented at the left; levels of expression of the proU-gfp transcriptional reporter fusion are given at the right (diagrams not to scale). Shown are the native proU promoter (A), proU with a functional VirB binding site at position −60 (B) or a mutated VirB binding site at the same position (C), and proU with a functional VirB binding site at position −270 with the URE removed (D) or with an inactivated VirB binding site at the same position (E). All constructs were assessed in S. flexneri for proU-gfp expression in a virB mutant (black bars), the wild type (white bars), and the hns mutant (gray bars) under conditions normally repressive of proU transcription.